TMEM106B is a receptor mediating ACE2-independent SARS-CoV-2 cell entry
- PMID: 37421949
- PMCID: PMC10409496
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.06.005
TMEM106B is a receptor mediating ACE2-independent SARS-CoV-2 cell entry
Abstract
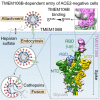
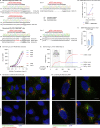
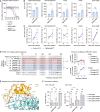
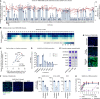
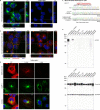
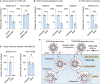
SARS-CoV-2 is associated with broad tissue tropism, a characteristic often determined by the availability of entry receptors on host cells. Here, we show that TMEM106B, a lysosomal transmembrane protein, can serve as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2 entry into angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)-negative cells. Spike substitution E484D increased TMEM106B binding, thereby enhancing TMEM106B-mediated entry. TMEM106B-specific monoclonal antibodies blocked SARS-CoV-2 infection, demonstrating a role of TMEM106B in viral entry. Using X-ray crystallography, cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM), and hydrogen-deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS), we show that the luminal domain (LD) of TMEM106B engages the receptor-binding motif of SARS-CoV-2 spike. Finally, we show that TMEM106B promotes spike-mediated syncytium formation, suggesting a role of TMEM106B in viral fusion. Together, our findings identify an ACE2-independent SARS-CoV-2 infection mechanism that involves cooperative interactions with the receptors heparan sulfate and TMEM106B.
Keywords: ACE2-independent entry; SARS-CoV-2; TMEM106B; TMEM106B crystal structure; antibody neutralization; coronavirus; cryo-EM; entry receptor.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.A.M., A.Y., E.B., M.R., M.A.Y.-C., N.F.-H., and T.N. are employees of Alector LLC, and H.R. was an Alector employee at the time of manuscript conception and may have an equity interest in Alector, Inc. Several authors have patents related to TMEM106B-specific antibodies. Work in the D.D. laboratory was partially funded by Alector LCC.
Figures
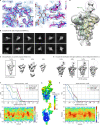

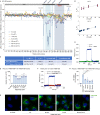
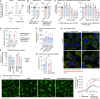
Comment in
-
Unveiling TMEM106B: SARS-CoV-2's secret entrance to the cell.Cell. 2023 Aug 3;186(16):3329-3331. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.005. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37541193
References
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Krüger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.H., Nitsche A., et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–280.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

