Arteriovenous malformation Map2k1 mutation affects vasculogenesis
- PMID: 37422456
- PMCID: PMC10329712
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-35301-6
Arteriovenous malformation Map2k1 mutation affects vasculogenesis
Abstract
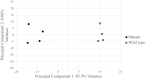
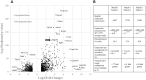
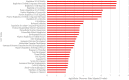
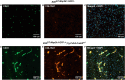
Somatic activating MAP2K1 mutations in endothelial cells (ECs) cause extracranial arteriovenous malformation (AVM). We previously reported the generation of a mouse line allowing inducible expression of constitutively active MAP2K1 (p.K57N) from the Rosa locus (R26GT-Map2k1-GFP/+) and showed, using Tg-Cdh5CreER, that EC expression of mutant MAP2K1 is sufficient for the development of vascular malformations in the brain, ear, and intestines. To gain further insight into the mechanism by which mutant MAP2K1 drives AVM development, we induced MAP2K1 (p.K57N) expression in ECs of postnatal-day-1 pups (P1) and investigated the changes in gene expression in P9 brain ECs by RNA-seq. We found that over-expression of MAP2K1 altered the transcript abundance of > 1600 genes. Several genes had > 20-fold changes between MAP2K1 expressing and wild-type ECs; the highest were Col15a1 (39-fold) and Itgb3 (24-fold). Increased expression of COL15A1 in R26GT-Map2k1-GFP/+; Tg-Cdh5CreER+/- brain ECs was validated by immunostaining. Ontology showed that differentially expressed genes were involved in processes important for vasculogenesis (e.g., cell migration, adhesion, extracellular matrix organization, tube formation, angiogenesis). Understanding how these genes and pathways contribute to AVM formation will help identify targets for therapeutic intervention.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Patent to treat AVM with MEK inhibitors (AKG, MLW). The remaining authors have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

