Synthesis and pharmacological activity of the epimers of hexahydrocannabinol (HHC)
- PMID: 37422571
- PMCID: PMC10329643
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-38188-5
Synthesis and pharmacological activity of the epimers of hexahydrocannabinol (HHC)
Abstract
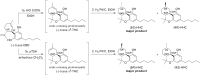
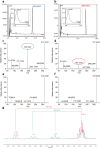
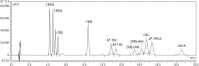
Cannabis is a multifaceted plant with numerous therapeutic properties on one hand, and controversial psychotropic activities on the other hand, which are modulated by CB1 endocannabinoid receptors. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) has been identified as the main component responsible for the psychotropic effects, while its constitutional isomer cannabidiol (CBD) has shown completely different pharmacological properties. Due to its reported beneficial effects, Cannabis has gained global popularity and is openly sold in shops and online. To circumvent legal restrictions, semi-synthetic derivatives of CBD are now frequently added to cannabis products, producing "high" effects similar to those induced by Δ9-THC. The first semi-synthetic cannabinoid to appear in the EU was obtained through cyclization and hydrogenation of CBD, and is known as hexahydrocannabinol (HHC). Currently, there is limited knowledge regarding HHC, its pharmacological properties, and its prevalence, as it is not commonly investigated in routine toxicological assays. In this study, synthetic strategies were explored to obtain an excess of the active epimer of HHC. Furthermore, the two epimers were purified and individually tested for their cannabinomimetic activity. Lastly, a simple and rapid chromatographic method employing a UV detector and a high-resolution mass spectrometer was applied to identify and quantify up to ten major phytocannabinoids, as well as the HHC epimers, in commercial cannabis samples.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro activation of the CB1 receptor by the semi-synthetic cannabinoids hexahydrocannabinol (HHC), hexahydrocannabinol acetate (HHC-O) and hexahydrocannabiphorol (HHC-P).Drug Test Anal. 2025 Apr;17(4):487-493. doi: 10.1002/dta.3750. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Drug Test Anal. 2025. PMID: 38894658 Free PMC article.
-
Hexahydrocannabinol and closely related semi-synthetic cannabinoids: A comprehensive review.Drug Test Anal. 2024 Feb;16(2):127-161. doi: 10.1002/dta.3519. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Drug Test Anal. 2024. PMID: 37269160 Review.
-
Investigation of the intrinsic cannabinoid activity of hemp-derived and semisynthetic cannabinoids with β-arrestin2 recruitment assays-and how this matters for the harm potential of seized drugs.Arch Toxicol. 2024 Aug;98(8):2619-2630. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03769-4. Epub 2024 May 12. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38735004
-
Hexahydrocannabinol Pharmacology, Toxicology, and Analysis: The First Evidence for a Recent New Psychoactive Substance.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023;21(12):2424-2430. doi: 10.2174/1570159X21666230623104624. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37357519 Free PMC article.
-
Using the BMD Approach to Derive Acceptable Daily Intakes of Cannabidiol (CBD) and Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Relevant to Electronic Cigarette Liquids.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Jul 25;27(8):228. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2708228. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36042166
Cited by
-
In vitro activation of the CB1 receptor by the semi-synthetic cannabinoids hexahydrocannabinol (HHC), hexahydrocannabinol acetate (HHC-O) and hexahydrocannabiphorol (HHC-P).Drug Test Anal. 2025 Apr;17(4):487-493. doi: 10.1002/dta.3750. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Drug Test Anal. 2025. PMID: 38894658 Free PMC article.
-
Human metabolism of the semi-synthetic cannabinoids hexahydrocannabinol, hexahydrocannabiphorol and their acetates using hepatocytes and urine samples.Drug Test Anal. 2025 Mar;17(3):372-386. doi: 10.1002/dta.3740. Epub 2024 May 28. Drug Test Anal. 2025. PMID: 38804224 Free PMC article.
-
An emerging trend in Novel Psychoactive Substances (NPSs): designer THC.J Cannabis Res. 2024 May 3;6(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s42238-024-00226-y. J Cannabis Res. 2024. PMID: 38702834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Potential of Synthetic Cannabinoids: Modulation of Biological Activity of Normal and Cancerous Human Colon Epithelial Cells.Cells. 2024 Sep 26;13(19):1616. doi: 10.3390/cells13191616. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39404380 Free PMC article.
-
Saturated Cannabinoids: Update on Synthesis Strategies and Biological Studies of These Emerging Cannabinoid Analogs.Molecules. 2023 Sep 4;28(17):6434. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176434. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- UNODC. World Drug Report 2021. (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

