Resourcefulness of propylprodigiosin isolated from Brevundimonas olei strain RUN-D1
- PMID: 37422847
- PMCID: PMC10329970
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-023-01579-y
Resourcefulness of propylprodigiosin isolated from Brevundimonas olei strain RUN-D1
Abstract
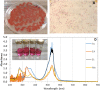
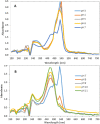
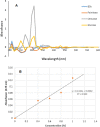
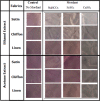
A novel red-pigmented bacterium was isolated from a water sample collected at Osun River, Ede. Morphological and 16 S rRNA gene sequencing revealed that the bacterium is a strain of Brevundimonas olei, while its red pigment was identified using UV-visible, FTIR and GCMS as a derivative of propylprodigiosin. The maximum absorbance of 534 nm, the FTIR's 1344 cm- 1 peak of prodigiosin's methoxyl C-O interaction, and the molecular ions from GCMS confirmed the pigment's identity. The pigments production was temperature-sensitive (25 °C), lost at > 28 °C, and in the presence of urea and humus. In addition, the pigment turned pink in the presence of hydrocarbons, while its red colour was retained with KCN and Fe2SO4, and enhanced by methylparaben. Furthermore, the pigment is stable in high temperature, salt, and acidic conditions, but changed to yellow in alkaline solution. The pigment, identified as propylprodigiosin (m/z 297), demonstrated broad-spectrum antibacterial activities against clinically important strains of Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC25923), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC9077), Bacillus cereus (ATCC10876), Salmonella typhi (ATCC13311), and Escherichia coli (DSM10974). The ethanol extract has the highest zones of inhibition of 29 ± 3.0, 26 ± 1.2, 22 ± 3.0, 22 ± 1.5, and 20 ± 2.0 mm, respectively. Furthermore, the acetone pigments interacted with cellulose and glucose such that increasing glucose concentrations showed linearity at 425 nm. Finally, the fastness of the pigments to fabrics was excellent, with percentage fadedness of 0 and - 43% light and washing tests, respectively, in the presence of Fe2SO4 as the mordant. The antibacterial nature of prodigiosin solutions and their good textile fastness to fabrics could be essential in manufacturing antiseptic materials such as bandages, hospital clothing and agricultural applications such as tubers preservation.Key points.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Biomarker; Percentage fadedness; Pigment; Prodigiosin; Textile dyes.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Affat SS. Classifications, advantages, disadvantages, toxicity effects of natural and synthetic dyes: a review. University Thi-Qar J Sci. 2021;8(1):130–135.
-
- Ahmad WA, Ahmad WYW, Zakaria ZA, Yusof NZ. Application of bacterial pigments as a colourant. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2012. pp. 57–74.
-
- Alijani Z, Amini J, Ashengroph M, Bahramnejad B. Antifungal activity of serratia rubidaea mar61-01 purified prodigiosin against colletotrichum nymphaea, the causal agent of strawberry anthracnose. J Plant Growth Regul. 2022;41:585–595. doi: 10.1007/s00344-021-10323-4. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

