Effect of 3-caffeoylquinic acid on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and intestinal functions in weaned pigs
- PMID: 37422911
- PMCID: PMC10393208
- DOI: 10.1093/jas/skad234
Effect of 3-caffeoylquinic acid on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and intestinal functions in weaned pigs
Abstract
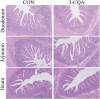
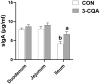
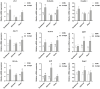
Phenolic acid like with the 3-caffeoylquini acid (3-CQA) is formed by caffeic acid and qunic acid. This study was conducted to explore the effect of 3-CQA on growth performance and intestinal functions in weaned pigs. A total of 180 weaned pigs were randomly allocated into five treatments with 6 replicate pens per treatment (6 pigs per pen). Pigs in the control group (CON) were fed with basal diet (BD), and the others in the experimental groups were fed with BD and supplemented with 12.5, 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg 3-CQA. On day 43, the blood sample-collected pigs in the CON and optimal-dose group (only based on growth performance) were picked, and housed in metabolism cages (a total of 12 pigs, N = 6). 3-CQA increased the feed efficiency from days 21 to 42 of the trial and throughout the trial (P < 0.05). 3-CQA increased the serum concentrations of total protein, albumin, and total cholesterol (P < 0.05). Moreover, 3-CQA supplementation at 25 mg/kg increased the apparent digestibility of DM, energy, and ash (P < 0.05). Interestingly, 3-CQA decreased the crypt depth but increased the ratio of villus height to crypt depth in the jejunum and ileum (P < 0.05). Moreover, 3-CQA also increased the activities of sucrase, lactase, and catalase in the jejunal mucosa, and increased the activities of alkaline phosphatase and superoxide dismutase in the ileal mucosa (P < 0.05). 3-CQA also increased the abundance of secretory immunoglobulin A in the ileal mucosa (P < 0.05). Importantly, 3-CQA not only elevated the expression levels of critical functional genes such as the zonula occludens-1 , occludin, solute carrier family 7 , and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in the duodenum but also elevated the expression levels of divalent metal transporter-1 and Nrf2 in the jejunum (P < 0.05). These results suggested a positive effect of 3-CQA supplementation on the growth and intestinal functions of weaned pigs. The mechanisms of action may be associated with elevated anti-oxidant capacity and improved intestinal barrier functions.
Keywords: 3-caffeoylquinic acid; anti-oxidant capacity; growth performance; intestinal functions; nutrient digestibility; weaned pigs.
Plain language summary
In last decades, swine producers used antibiotics as growth promoter added into diet. However, the pharmaceutical use of antibiotics is prohibited by the legislation of several countries due to potential health and environmental concerns. Therefore, the development of substitutes for traditionally used antibiotics has attracted considerable research interest worldwide. Natural phnolic acid like with the 3-CQA is an important component of biologically active phenols isolated from various natural plants. This study was carried out to evaluate the effect of 3-CQA on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, and intestinal functions in pigs. Results indicated that dietary 3-CQA supplementation improved the growth performance, nutrients digestibility in weaned pigs. The beneficial effects of 3-CQA supplementation on growth and intestinal functions suggested that it could serve as a natural potent substitute for antibiotics.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society of Animal Science. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no real or perceived conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of cordyceps militaris on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal epithelium functions in weaned pigs.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae194. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae194. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39001695 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary chlorogenic acid improves growth performance of weaned pigs through maintaining antioxidant capacity and intestinal digestion and absorption function.J Anim Sci. 2018 Apr 3;96(3):1108-1118. doi: 10.1093/jas/skx078. J Anim Sci. 2018. PMID: 29562339 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of an organic acid blend as an antibiotic alternative on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, intestinal barrier function, and fecal microbiota in weaned piglets.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae149. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae149. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 38863369 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Lactobacillus reuteri LR1 on the growth performance, intestinal morphology, and intestinal barrier function in weaned pigs.J Anim Sci. 2018 Jun 4;96(6):2342-2351. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky129. J Anim Sci. 2018. PMID: 29659876 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Biological function of resveratrol and its application in animal production: a review.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 11;14(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40104-022-00822-z. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36765425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of coated-benzoic acid on growth performance, immunity, and intestinal functions in weaned pigs challenged by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Sep 16;11:1430696. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1430696. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39351150 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterization and Toxicological Study of Proanthocyanidins in Weaned Pigs.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Sep 7;15(9):558. doi: 10.3390/toxins15090558. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AOAC. 2016. Official methods of analysis. 15th ed. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem., Arlington, VA.
-
- Bai, D., Liu K., He X., Tan H., Liu Y., Li Y., Zhang Y., Zhen W., Zhang C., and Ma Y.. . 2022. Effect of Dietary Chlorogenic Acid on Growth Performance, Antioxidant Function, and Immune Response of Broiler Breeders under Immune Stress and Stocking Density Stress. Veterinary Sciences 9:582. .10.3390/vetsci9100582 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

