Cellular allostatic load is linked to increased energy expenditure and accelerated biological aging
- PMID: 37423094
- PMCID: PMC10528419
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2023.106322
Cellular allostatic load is linked to increased energy expenditure and accelerated biological aging
Abstract
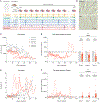
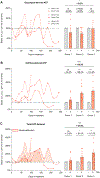
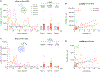
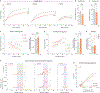
Stress triggers anticipatory physiological responses that promote survival, a phenomenon termed allostasis. However, the chronic activation of energy-dependent allostatic responses results in allostatic load, a dysregulated state that predicts functional decline, accelerates aging, and increases mortality in humans. The energetic cost and cellular basis for the damaging effects of allostatic load have not been defined. Here, by longitudinally profiling three unrelated primary human fibroblast lines across their lifespan, we find that chronic glucocorticoid exposure increases cellular energy expenditure by ∼60%, along with a metabolic shift from glycolysis to mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos). This state of stress-induced hypermetabolism is linked to mtDNA instability, non-linearly affects age-related cytokines secretion, and accelerates cellular aging based on DNA methylation clocks, telomere shortening rate, and reduced lifespan. Pharmacologically normalizing OxPhos activity while further increasing energy expenditure exacerbates the accelerated aging phenotype, pointing to total energy expenditure as a potential driver of aging dynamics. Together, our findings define bioenergetic and multi-omic recalibrations of stress adaptation, underscoring increased energy expenditure and accelerated cellular aging as interrelated features of cellular allostatic load.
Keywords: Aging; Allostatic load; Chronic stress; Epigenetic aging; Glucocorticoid; Hypermetabolism; Mitochondria; Telomere.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures





References
-
- Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker S, 2015. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw 67, 1–48.
-
- Blanckenhorn WU, 2000. The evolution of body size: what keeps organisms small? Q. Rev. Biol 75, 385–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

