The NephroCheck bedside system for detecting stage 3 acute kidney injury after open thoracoabdominal aortic repair
- PMID: 37423933
- PMCID: PMC10330159
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-38242-2
The NephroCheck bedside system for detecting stage 3 acute kidney injury after open thoracoabdominal aortic repair
Abstract
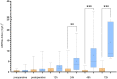
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication after complex aortic procedures and it is associated with relevant mortality and morbidity. Biomarkers for early and specific AKI detection are lacking. The aim of this work is to investigate the reliability of the NephroCheck bedside system for diagnosing stage 3 AKI following open aortic surgery. In this prospective, multicenter, observational study,- https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04087161 -we included 45 patients undergoing open thoracoabdominal aortic repair. AKI risk (AKIRisk-Index) was calculated from urine samples at 5 timepoints: baseline, immediately postoperatively and at 12, 24, 48, and 72 h post-surgery. AKIs were classified according to the KDIGO criteria. Contributing factors were identified in univariable and multivariable logistic regression. Predictive ability was assessed with the area under the receiver operator curve (ROCAUC). Among 31 patients (68.8%) that developed AKIs, 21 (44.9%) developed stage-3 AKIs, which required dialysis. AKIs were correlated with increased in-hospital mortality (p = .006), respiratory complications (p < .001), sepsis (p < .001), and multi-organ dysfunction syndrome (p < .001). The AKIRisk-Index showed reliable diagnostic accuracy starting at 24 h post-surgery (ROCAUC: .8056, p = .001). In conclusion, starting at 24 h after open aortic repair, the NephroCheck system showed adequate diagnostic accuracy for detecting the patients at risk for stage 3 AKIs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Brown JR, Cochran RP, Dacey LJ, Ross CS, Kunzelman KS, Dunton RF, et al. Perioperative increases in serum creatinine are predictive of increased 90-day mortality after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Circulation. 2006;114(1 Suppl):I409–I413. - PubMed
-
- Oezkur M, Magyar A, Thomas P, Stork T, Schneider R, Bening C, et al. TIMP-2*IGFBP7 (Nephrocheck(R)) measurements at intensive care unit admission after cardiac surgery are predictive for acute kidney injury within 48 hours. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017;42(3):456–467. doi: 10.1159/000479298. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

