Evaluation of Resident Palpation Skills in Foot and Ankle Anatomic Structures Using Bedside Ultrasound
- PMID: 37424710
- PMCID: PMC10324702
- DOI: 10.36518/2689-0216.1029
Evaluation of Resident Palpation Skills in Foot and Ankle Anatomic Structures Using Bedside Ultrasound
Abstract
Objective: The objective is to determine the accuracy of foot and ankle joint and soft tissue structure palpation in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (PM&R) residents using ultrasonography (US) verification.
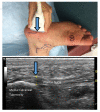
Methods: PM&R residents were tested in an outpatient musculoskeletal (MSK) clinic on palpated foot and ankle anatomic structures in a human model. Once the presumed structures were localized, residents marked a 1 cm size circle on the overlying skin with a ink marker. The accuracy of the circle over the joint line and soft tissue structures was verified using US.
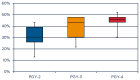
Results: The overall palpation accuracy for 22 joint line and soft tissue structures was 38.0%. Accuracy by foot and ankle region, including the posterior, medial, lateral, plantar, and dorsal were 72.9%, 47.5%, 42.5%, 35% and 7.8% respectively. There was a positive trend with level of education without a statistically significant difference in palpation accuracy (30.4% in PGY-2, 38.3% in PGY-3, 44.2% in PGY-4, p = 0.11).
Conclusions: Residents in this study demonstrated suboptimal accuracy of foot and ankle anatomic structure identification by palpation. US may be a useful adjunctive tool to advance current methods of teaching musculoskeletal examination skills to PM&R residents.
Keywords: diagnostic imaging; foot and ankle; graduate medical education; musculoskeletal system; physical examination; physical medicine and rehabilitation medicine; ultrasonography.
© 2020 HCA Physician Services, Inc. d/b/a Emerald Medical Education.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Localization of Hand and Wrist Anatomic Structures Among Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Residents: Implication of Ultrasonography in Palpation Skill Verification.HCA Healthc J Med. 2021 Apr 28;2(2):115-121. doi: 10.36518/2689-0216.1189. eCollection 2021. HCA Healthc J Med. 2021. PMID: 37425638 Free PMC article.
-
Resident accuracy of joint line palpation using ultrasound verification.PM R. 2014 Oct;6(10):920-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2014.02.006. Epub 2014 Feb 14. PM R. 2014. PMID: 24534099
-
Identifying and Monitoring Deficiencies in Physical Examination of the Foot and Ankle With Diagnostic Ultrasound: Experience From a Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Residency Training Program.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020 Oct;99(10):961-967. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000001425. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 32195736
-
Musculoskeletal ultrasound of the ankle and foot.Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2010 Aug;21(3):549-57. doi: 10.1016/j.pmr.2010.06.002. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2010. PMID: 20797549 Review.
-
Ultrasound of the ankle and foot in rheumatology.Med Ultrason. 2012 Mar;14(1):34-41. Med Ultrason. 2012. PMID: 22396937 Review.
Cited by
-
Localization of Hand and Wrist Anatomic Structures Among Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Residents: Implication of Ultrasonography in Palpation Skill Verification.HCA Healthc J Med. 2021 Apr 28;2(2):115-121. doi: 10.36518/2689-0216.1189. eCollection 2021. HCA Healthc J Med. 2021. PMID: 37425638 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
