A chromosomal reference genome sequence for the malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae, Giles, 1902, Ifakara strain
- PMID: 37424773
- PMCID: PMC10326452
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.18854.2
A chromosomal reference genome sequence for the malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae, Giles, 1902, Ifakara strain
Abstract
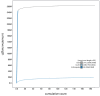
We present a genome assembly from an individual female Anopheles gambiae (the malaria mosquito; Arthropoda; Insecta; Diptera; Culicidae), Ifakara strain. The genome sequence is 264 megabases in span. Most of the assembly is scaffolded into three chromosomal pseudomolecules with the X sex chromosome assembled. The complete mitochondrial genome was also assembled and is 15.4 kilobases in length.
Keywords: African malaria mosquito; Anopheles gambiae; chromosomal; genome sequence.
Copyright: © 2024 Habtewold T et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures




References
-
- Besansky NJ: Proposal for the Eight Genomes Cluster for Genus Anopheles .2004. Reference Source
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

