USP37 promotes angiogenesis and metastasis in colorectal cancer by facilitating β-catenin stability
- PMID: 37424824
- PMCID: PMC10326571
USP37 promotes angiogenesis and metastasis in colorectal cancer by facilitating β-catenin stability
Abstract
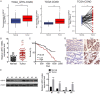
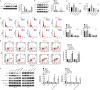
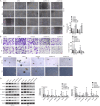
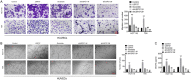
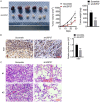
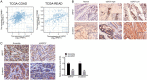
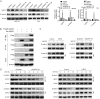
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 37 (USP37) is a novel deubiquitinating enzyme, which has been found to be involved in the progression of multiple tumors. However, its function in colorectal cancer (CRC) remains unclear. Here, we firstly proved that USP37 was up-regulated in CRC cases, and high USP37 expression predicted poor survival of CRC cases. USP37 up-regulation promoted the proliferation, cell cycle progression, apoptosis inhibition, migration, invasion, epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) and stemness of CRC cells; moreover, USP37 facilitated the angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). However, USP37 silencing showed the opposite function. In vivo experiment suggested that USP37 silencing suppressed the growth and lung metastasis of CRC in nude mice. Interestingly, we found that CTNNB1 (gene coding for β-catenin) level was positively correlated with USP37 level in CRC and USP37 silencing suppressed the expression of β-catenin in CRC cells and xenograft tumor tissues. Further mechanistic studies showed that USP37 could enhance the stability of β-catenin by inhibiting its ubiquitination. Taken together, USP37 acts as an oncogene in CRC, which promotes angiogenesis, metastasis and stemness by enhancing β-catenin stability via inhibiting its ubiquitination. USP37 may be a usefully target in CRC clinical treatment.
Keywords: CRC; USP37; angiogenesis; metastasis; β-catenin stability.
AJCR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Si H, Yang Q, Hu H, Ding C, Wang H, Lin X. Colorectal cancer occurrence and treatment based on changes in intestinal flora. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;70:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL, Siegel RL. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:363–385. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
