Fibroblast growth factor 21 resistance is associated with body shape in patients with type 2 diabetes complicating hypertension
- PMID: 37424900
- PMCID: PMC10325616
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1168047
Fibroblast growth factor 21 resistance is associated with body shape in patients with type 2 diabetes complicating hypertension
Abstract
Objectives: Obesity, especially abdominal obesity, increases the prevalence of metabolic and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has been identified as a critical regulator playing a therapeutic role in diabetes and its complications. This study aims to evaluate the relationship between serum FGF21 levels and body shape parameters in patients with hypertension (HP) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods: Serum FGF21 levels were determined in 1,003 subjects, including 745 patients with T2DM, and 258 individuals were selected as a healthy control in this cross-sectional study.
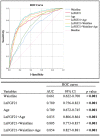
Results: Serum FGF21 levels were significantly higher in T2DM patients with HP than those without [534.9 (322.6-722.2) vs. 220.65 (142.8-347.55) pg/ml, p < 0.001], and levels in both of these two groups were significantly increased compared with that of healthy control [123.92 (67.23-219.32) pg/ml, all p < 0.001]. These differences were also observed in body shape parameters, including weight, waistline, body mass index (BMI), body shape index (ABSI), and the percentage of abdominal obesity. Serum FGF21 levels in T2DM patients were positively correlated with body shape parameters, including weight, waistline, neck circumference, BMI, ABSI, percent of abdominal obesity, and triglyceride, while negatively with estimated glomerular filtration rate (all p < 0.01). The significance remained stable when adjusted for age and T2DM duration. In addition, both serum FGF21 concentrations and waistline were independently associated with HP in T2DM patients after the adjustment for risk factors (all p < 0.05). ROC analysis for FGF21 levels of 745 patients with T2DM identified 411.33 pg/ml as an optimal cut-off point to predict HP, with a sensitivity and specificity of 66.0% and 84.9%, respectively.
Conclusions: FGF21 resistance occurs in patients of HP in T2DM, and positively correlates with body shape parameters (especially waistline and BMI). High levels of FGF21 may be a compensatory reaction to offset HP.
Keywords: FGF21 resistance; body shape; hypertension; type 2 diabetes mellitus; waistline.
© 2023 Gan, Duan, Tang, Liu, Tian, Wu, Bi, Pan, Wang, Gao, Wang, Lin and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased circulating FGF21 level predicts the burden of metabolic demands and risk of vascular diseases in adults with type 2 diabetes.BMC Endocr Disord. 2023 Dec 7;23(1):272. doi: 10.1186/s12902-023-01523-y. BMC Endocr Disord. 2023. PMID: 38057786 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels Are Positively Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Endocrinol. 2019 Sep 10;2019:5163245. doi: 10.1155/2019/5163245. eCollection 2019. Int J Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 31582974 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Fetuin-A in Obese Adolescents With and Without Type 2 Diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Aug;100(8):3004-10. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-2192. Epub 2015 Jun 8. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26052728
-
Role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in gestational diabetes mellitus: A mini-review.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019 Jan;90(1):47-55. doi: 10.1111/cen.13881. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 30346647 Review.
-
Biological role, clinical significance, and therapeutic possibilities of the recently discovered metabolic hormone fibroblastic growth factor 21.Eur J Endocrinol. 2012 Sep;167(3):301-9. doi: 10.1530/EJE-12-0357. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22740503 Review.
Cited by
-
CAVIN-2 positively correlates with diabetic PAD and promotes LDL transcytosis by inhibiting eNOS activation.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2457526. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2457526. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39887709 Free PMC article.
-
Higher circulating FGF21, lower protein intake, and lower muscle mass: Associations with a higher risk of mortality.J Intern Med. 2025 Jul;298(1):2-15. doi: 10.1111/joim.20099. Epub 2025 May 19. J Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 40390366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu YK, Ling S, Lui LMW, Ceban F, Vinberg M, Kessing LV, et al. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, impaired fasting glucose, general obesity, and abdominal obesity in patients with bipolar disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. (2022) 300:449–61. 10.1016/j.jad.2021.12.110 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous