Lakeshore vegetation: More resilient towards human recreation than we think?
- PMID: 37424934
- PMCID: PMC10329258
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.10268
Lakeshore vegetation: More resilient towards human recreation than we think?
Abstract
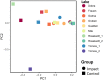
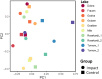
Lakes and their shoreline vegetation are rich in biodiversity and provide multiple functions and habitats for fauna and flora. Humans are attracted by the scenic beauty of these ecosystems and the possibilities for recreational activities they offer. However, the use of lakes for recreational activities can lead to disturbance of vegetation, threatening the integrity and functionality of shoreline areas. Recent literature reviews revealed that impacts of the seemingly harmless activities bathing and lingering on the shore on lakeshore vegetation are poorly understood. In this study, we analysed the effects of shoreline use connected with bathing on the structure, composition and diversity of lakeshore vegetation. Vegetation relevés were recorded in 10 bathing and 10 adjacent control sites in the nature park 'Dahme-Heideseen' (Brandenburg, Germany). In addition visitor counts were performed. The species composition and the cover of herbaceous and shrub vegetation differed between bathing and control sites, but all sites had a high percentage of plant species not typical for the community. The vegetation parameters did not correlate with visitor counts. The results indicate that the present visitor intensity in the nature park does not impact the vegetation severely.
Keywords: biodiversity; ecological impacts; freshwater; recreation ecology; shoreline vegetation.
© 2023 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Allaby, M. (2010). Shannon–wiener index of diversity. In A dictionary of ecology. Oxford University Press. https://www.oxfordreference.com/view/10.1093/acref/9780199567669.001.000... - DOI
-
- Andersen, U. V. (1995). Resistance of Danish coastal vegetation types to human trampling. Biological Conservation, 71(3), 223–230. 10.1016/0006-3207(94)00031-K - DOI
-
- Andrés‐Abellán, M. , Del Benayas Álamo, J. , Landete‐Castillejos, T. , Lopéz‐Serrano, F. R. , García‐Morote, F. A. , & Del Cerro‐Barja, A. (2005). Impacts of visitors on soil and vegetation of the recreational area "Nacimiento del Rio Mundo" (Castilla‐La Mancha, Spain). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 101(1), 55–67. 10.1007/s10661-005-9130-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bayfield, N. G. (1979). Recovery of four montane heath communities on Cairngorm, Scotland, from disturbance by trampling. Biological Conservation, 15(3), 165–179. 10.1016/0006-3207(79)90038-7 - DOI
-
- Berg, C. , & Dengler, J. (2005). Moose und Flechten als diagnostische Arten von Pflanzengesellschaften – Eine Übersicht aus Mecklenburg‐Vorpommern, 17.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

