Neural lineage differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells: Advances in disease modeling
- PMID: 37424945
- PMCID: PMC10324500
- DOI: 10.4252/wjsc.v15.i6.530
Neural lineage differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells: Advances in disease modeling
Abstract
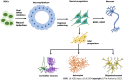
Brain diseases affect 1 in 6 people worldwide. These diseases range from acute neurological conditions such as stroke to chronic neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. Recent advancements in tissue-engineered brain disease models have overcome many of the different shortcomings associated with the various animal models, tissue culture models, and epidemiologic patient data that are commonly used to study brain disease. One innovative method by which to model human neurological disease is via the directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) to neural lineages including neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. Three-dimensional models such as brain organoids have also been derived from hPSCs, offering more physiological relevance due to their incorporation of various cell types. As such, brain organoids can better model the pathophysiology of neural diseases observed in patients. In this review, we will emphasize recent developments in hPSC-based tissue culture models of neurological disorders and how they are being used to create neural disease models.
Keywords: Assembloids; Astrocytes; Brain organoids; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Microglia; Oligodendrocytes.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Lauren E Woodard and Julie Bejoy have two patent applications submitted on “Accelerated protocol for deriving podocytes from hiPSCs” and “nephron progenitor exosomes” listed below; Inventors: Bejoy J and Woodard LE accelerated the protocol for the differentiation of podocytes from human pluripotent stem cells. Patent Application filed August 26, 2022. PCT/US2022/075447; Inventors: Bejoy J and Woodard LE Nephron progenitor exosomes, patent Application filed October 6, 2022. PCT/US2022/077692.
Figures

References
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M, Ichisaka T, Tomoda K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell . 2007;131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell . 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Takasato M, Er PX, Chiu HS, Maier B, Baillie GJ, Ferguson C, Parton RG, Wolvetang EJ, Roost MS, Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM, Little MH. Kidney organoids from human iPS cells contain multiple lineages and model human nephrogenesis. Nature . 2015;526:564–568. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Wang H, Deng P, Chen W, Guo Y, Tao T, Qin J. In situ differentiation and generation of functional liver organoids from human iPSCs in a 3D perfusable chip system. Lab Chip . 2018;18:3606–3616. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

