Pattern breaking: a complex systems approach to psychedelic medicine
- PMID: 37424966
- PMCID: PMC10325487
- DOI: 10.1093/nc/niad017
Pattern breaking: a complex systems approach to psychedelic medicine
Abstract
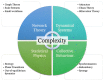
Recent research has demonstrated the potential of psychedelic therapy for mental health care. However, the psychological experience underlying its therapeutic effects remains poorly understood. This paper proposes a framework that suggests psychedelics act as destabilizers, both psychologically and neurophysiologically. Drawing on the 'entropic brain' hypothesis and the 'RElaxed Beliefs Under pSychedelics' model, this paper focuses on the richness of psychological experience. Through a complex systems theory perspective, we suggest that psychedelics destabilize fixed points or attractors, breaking reinforced patterns of thinking and behaving. Our approach explains how psychedelic-induced increases in brain entropy destabilize neurophysiological set points and lead to new conceptualizations of psychedelic psychotherapy. These insights have important implications for risk mitigation and treatment optimization in psychedelic medicine, both during the peak psychedelic experience and during the subacute period of potential recovery.
Keywords: complex systems theory; entropic brain; free-energy principle; psychedelics; psychological experience.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
With great power comes great vulnerability: an ethical analysis of psychedelics' therapeutic mechanisms proposed by the REBUS hypothesis.J Med Ethics. 2023 Nov 23;49(12):826-832. doi: 10.1136/jme-2022-108816. J Med Ethics. 2023. PMID: 37045591
-
Psychedelics, entropic brain theory, and the taxonomy of conscious states: a summary of debates and perspectives.Neurosci Conscious. 2023 Apr 4;2023(1):niad001. doi: 10.1093/nc/niad001. eCollection 2023. Neurosci Conscious. 2023. PMID: 37025356 Free PMC article.
-
How Psychedelic-Assisted Treatment Works in the Bayesian Brain.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Mar 8;13:812180. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.812180. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35360137 Free PMC article.
-
The Evolved Psychology of Psychedelic Set and Setting: Inferences Regarding the Roles of Shamanism and Entheogenic Ecopsychology.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Feb 23;12:619890. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.619890. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33732156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-Entropic Broadening Theory: Toward a New Understanding of Self and Behavior Change Informed by Psychedelics and Psychosis.Pharmacol Rev. 2022 Oct;74(4):982-1027. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.121.000514. Pharmacol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36113878 Review.
Cited by
-
From taboo to treatment: The emergence of psychedelics in the management of pain and opioid use disorder.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Dec;90(12):3036-3053. doi: 10.1111/bcp.16045. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38627909 Review.
-
Neural Geometrodynamics, Complexity, and Plasticity: A Psychedelics Perspective.Entropy (Basel). 2024 Jan 22;26(1):0. doi: 10.3390/e26010090. Entropy (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275498 Free PMC article.
-
Shifting boundaries, extended minds: ambient technology and extended allostatic control.Synthese. 2025;205(2):81. doi: 10.1007/s11229-025-04924-9. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Synthese. 2025. PMID: 39926591 Free PMC article.
-
Meditation and complexity: a review and synthesis of evidence.Neurosci Conscious. 2025 May 28;2025(1):niaf013. doi: 10.1093/nc/niaf013. eCollection 2025. Neurosci Conscious. 2025. PMID: 40438122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring psychedelic-assisted therapy in the treatment of functional seizures: A review of underlying mechanisms and associated brain networks.J Psychopharmacol. 2024 May;38(5):407-416. doi: 10.1177/02698811241248395. Epub 2024 Apr 23. J Psychopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38654554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aday JS, Mitzkovitz CM, Bloesch EK. et al. Long-term effects of psychedelic drugs: a systematic review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2020;113:179–89. - PubMed
-
- Ambika G, Kurths J. Tipping in complex systems: theory, methods and applications. Eur Phys J Spec Top 2021;230:3177–9.
