A Retrospective Comparison of the Effectiveness of Buprenorphine Versus Baclofen for Acute Opioid Withdrawal
- PMID: 37424975
- PMCID: PMC10324876
- DOI: 10.36518/2689-0216.1498
A Retrospective Comparison of the Effectiveness of Buprenorphine Versus Baclofen for Acute Opioid Withdrawal
Abstract
Background: A significant impediment to opioid cessation or dose reduction is mitigating withdrawal severity that has been shown to affect the course of opioid dependence. Current guidelines recommend the use of buprenorphine and methadone over alpha-2 adrenergic agonists. Baclofen, a GABA-B agonist, has promising results as an adjunct agent for opioid withdrawal but has not been compared to buprenorphine. This study compared the ability of buprenorphine and baclofen to mitigate acute opioid withdrawal.
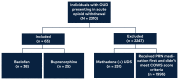
Methods: This was a single-center, retrospective chart review of 63 patients with diagnosed opioid use disorder that received scheduled buprenorphine or baclofen for 3 days, in addition to as-needed medications during 2 distinct time periods (pre-2017 and 2017-2020). Patients were admitted to the inpatient detoxification unit at Gateway Community Services in Jacksonville, FL.
Results: The results showed that patients achieving detoxification success were 11.2 times more likely to be exposed to baclofen than buprenorphine (95% CI 3.32 - 37.83, P < .001). Completion of detoxification protocol (baclofen 63.2% vs buprenorphine 72%, P = .649) and incidence of orthostatic hypotension (15.8% versus 0%, P = .073) were not significantly different between the 2 groups.
Conclusion: Patients treated with baclofen had a lower frequency of secondary medication use for acute opioid withdrawal than patients treated with buprenorphine. This raises an interesting question of whether baclofen is comparable to buprenorphine for treating opioid withdrawal. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial in a larger patient population is warranted to determine this difference.
Keywords: baclofen; buprenorphine; inpatient detoxification; opioid withdrawal; opioid-related disorders; opioid-related disorders/therapy; substance abuse treatment centers; substance withdrawal syndrome.
© 2023 HCA Physician Services, Inc. d/b/a Emerald Medical Education.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Understanding drug overdoses and deaths. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; [Accessed July 24, 2020]. Updated February 14, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/epidemic/index.html .
-
- HCUP fast stats: Opioid-related hospital use, national & state. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; [Accessed July 24, 2020]. https://datatools.ahrq.gov/hcup-fast-stats?tab=hcupfsse&type=tab .
-
- Reported law enforcement encounters testing positive for fentanyl increase across US. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; [Accessed July 24, 2020]. Updated August 9, 2021 https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/deaths/fentanyl-encounters/index.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
