Influencing factors associated with high myopia in Chinese college students
- PMID: 37425324
- PMCID: PMC10326280
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1146291
Influencing factors associated with high myopia in Chinese college students
Abstract
Background: High myopia (HM) may elicit irreversible pathological changes in the fundus and severely impair visual quality, thereby becoming a major public health issue in China. However, the influencing factors associated with HM remain unknown in Chinese college students, whose visual quality is crucial to country development.
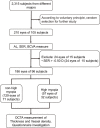
Methods: This is a cross-sectional observational study. Two thousand three hundred and fifteen undergraduate and graduate students were initially recruited from various majors in 3 universities in Tianjin, China. Under the principle of voluntary participation and informed consent, simple random sampling was conducted in the recruited subjects while maintaining balanced number of subjects from each major. After screening with inclusion and exclusion criteria, 96 undergraduate and graduate students (186 eyes) were finally included and divided into non-HM and HM groups. The eyes of subjects were examined by optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) for vessel density and structure thickness at the macula and optic disc, and the subjects were surveyed by an itemized questionnaire on lifestyles and study habits.
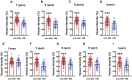
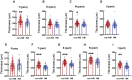
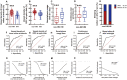
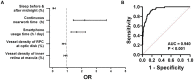
Results: The OCTA and questionnaire results revealed 10 factors, including hemodynamic and anatomic parameters and lifestyle metrics, with statistical significance between the non-HM and HM groups. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that vessel density of the inner retina at the macula, vessel density of the radial peripapillary capillary at the optic disc, smartphone usage time, continuous near work time, and sleeping after midnight had superior values of area under the curve (AUC > 0.700). Therefore, these 5 factors were selected for univariant and multivariant logistic regression analyses. A prediction model comprising the 5 influencing factors had an AUC of 0.940 and 95% CI of 0.908-0.972.
Conclusion: This study for the first time identified the vessel density of the inner retina at the macula, the vessel density of the radial peripapillary capillary at the optic disc, smartphone usage time, continuous near work time, and sleeping after midnight as influencing factors associated with HM in Chinese college students. A prediction model comprising the 5 influencing factors was proposed for calculating likelihood of a Chinese college student developing HM, based on which lifestyle improvement and medical intervention might be recommended.
Keywords: habits; influencing factor; lifestyles; myopia; retinal thickness; vessel density.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Hou, Li, Wang, Liu, Zhang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Retinal microvasculature and optic disc alterations in non-pathological high myopia with optical coherence tomography angiography.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov;259(11):3221-3227. doi: 10.1007/s00417-021-05216-x. Epub 2021 May 7. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33961111
-
The Deep Vascular Plexus Density Is Closely Related to Myopic Severity.Ophthalmic Res. 2022;65(4):455-465. doi: 10.1159/000523938. Epub 2022 Mar 16. Ophthalmic Res. 2022. PMID: 35294948
-
Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography of Optic Disc and Macula Vessel Density in Glaucoma and Healthy Eyes.J Glaucoma. 2019 Jan;28(1):80-87. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0000000000001125. J Glaucoma. 2019. PMID: 30461553
-
A Meta-Analysis of Alterations in the Retina and Choroid in High Myopia Assessed by Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography.Ophthalmic Res. 2021;64(6):928-937. doi: 10.1159/000517096. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Ophthalmic Res. 2021. PMID: 34237732
-
Macular and peripapillary vessel density in myopic eyes of young Chinese adults.Clin Exp Optom. 2020 Nov;103(6):830-837. doi: 10.1111/cxo.13047. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Clin Exp Optom. 2020. PMID: 32052475
Cited by
-
The Effect of Partial Sleep Deprivation on Retinal Microvasculature in Myopia With Different Axial Lengths.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Mar 3;66(3):57. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.3.57. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40146130 Free PMC article.
-
Digital Screen Time and Myopia: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 Feb 3;8(2):e2460026. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.60026. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 39982728 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

