Influence of antipsychotic medications on hyperlipidemia risk in patients with schizophrenia: evidence from a population-based cohort study and in vitro hepatic lipid homeostasis gene expression
- PMID: 37425327
- PMCID: PMC10324036
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1137977
Influence of antipsychotic medications on hyperlipidemia risk in patients with schizophrenia: evidence from a population-based cohort study and in vitro hepatic lipid homeostasis gene expression
Abstract
Introduction: Schizophrenia increases the risk of mortality and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk. However, the correlation between antipsychotics (APs) and CVD remains controversial. Hyperlipidemia is a significant risk factor for CVD.
Methods: We conducted a nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study to investigate the effects of APs on the risk of hyperlipidemia and lipid homeostasis gene expression. We used data from the Longitudinal Health Insurance Database of Taiwan on new-onset schizophrenia patients and a comparison cohort without schizophrenia. We used a Cox proportional hazards regression model to analyze the differences in hyperlipidemia development between the two cohorts. Furthermore, we examined the effects of APs on the hepatic expression of lipid homeostasis-related genes.
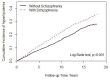
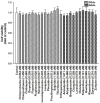
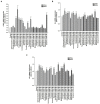
Results: After adjusting for potential interrelated confounding factors, the case group (N = 4,533) was found to have a higher hyperlipidemia risk than the control cohort (N = 4,533) [adjusted hazard ratio (aHR), 1.30, p < 0.001]. Patients with schizophrenia without APs had a significantly higher risk of hyperlipidemia (aHR, 2.16; p < 0.001). However, patients receiving APs had a significantly lower risk of hyperlipidemia than patients not receiving APs (all aHR ≤ 0.42, p < 0.001). First-generation antipsychotics (FGAs) induce the expression of hepatic lipid catabolism genes in an in vitro model.
Discussion: Patients with schizophrenia had a higher risk of hyperlipidemia than controls; however, compared with non-treated patients, AP users had a lower risk of hyperlipidemia. Early diagnosis and management of hyperlipidemia may help prevent CVD.
Keywords: antipsychotic medications; cohort study; hyperlipidemia; lipid homeostasis; schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2023 Wu, Tien, Lin, Cheah, Hsu, Tsai, Fang and Lim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influences of antidepressant medications on the risk of developing hyperlipidemia in patients with depression by a population-based cohort study and on in vitro hepatic lipogenic-related gene expression.J Affect Disord. 2021 Dec 1;295:271-283. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.08.041. Epub 2021 Aug 26. J Affect Disord. 2021. PMID: 34482059
-
Impact of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and IBD Medications on Risk of Hyperlipidemia and in vitro Hepatic Lipogenic-Related Gene Expression: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 13;9:910623. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.910623. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35770006 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Urate-Lowering Therapy on Risk of Hyperlipidemia in Gout by a Population-Based Cohort Study and on In Vitro Hepatic Lipogenesis-Related Gene Expression.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Nov 14;2020:8890300. doi: 10.1155/2020/8890300. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 33273891 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and related metabolic abnormalities during antipsychotic drug administration: mechanisms, management and research perspectives.Pharmacopsychiatry. 2002 Nov;35(6):205-19. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-36391. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2002. PMID: 12518268 Review.
-
[Schizophrenia, diabetes mellitus and antipsychotics].Encephale. 2004 Jul-Aug;30(4):382-91. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(04)95452-8. Encephale. 2004. PMID: 15538314 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Structural insights into novel therapeutic deep eutectic systems with capric acid using 1D, 2D NMR and DSC techniques with superior gut permeability.RSC Adv. 2024 May 7;14(21):14793-14806. doi: 10.1039/d4ra01469c. eCollection 2024 May 2. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38716106 Free PMC article.
-
Association of antipsychotic drugs on type 2 diabetes mellitus risk in patients with schizophrenia: a population-based cohort and in vitro glucose homeostasis-related gene expression study.BMC Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 30;24(1):751. doi: 10.1186/s12888-024-06222-z. BMC Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39472855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sahoo S, Ameen S, Akhtar S. Metabolic syndrome in drug-naïve first-episode psychosis treated with atypical antipsychotics. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. (2007) 41:629. PMID: - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

