A versatile genomic transgenesis platform with enhanced λ integrase for human Expi293F cells
- PMID: 37425360
- PMCID: PMC10325659
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1198465
A versatile genomic transgenesis platform with enhanced λ integrase for human Expi293F cells
Abstract
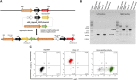
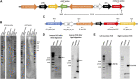
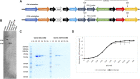
Reliable cell-based platforms to test and/or produce biologics in a sustainable manner are important for the biotech industry. Utilizing enhanced λ integrase, a sequence-specific DNA recombinase, we developed a novel transgenesis platform involving a fully characterized single genomic locus as an artificial landing pad for transgene insertion in human Expi293F cells. Importantly, transgene instability and variation in expression were not observed in the absence of selection pressure, thus enabling reliable long-term biotherapeutics testing or production. The artificial landing pad for λ integrase can be targeted with multi-transgene constructs and offers future modularity involving additional genome manipulation tools to generate sequential or nearly seamless insertions. We demonstrated broad utility with expression constructs for anti PD-1 monoclonal antibodies and showed that the orientation of heavy and light chain transcription units profoundly affected antibody expression levels. In addition, we demonstrated encapsulation of our PD-1 platform cells into bio-compatible mini-bioreactors and the continued secretion of antibodies, thus providing a basis for future cell-based applications for more effective and affordable therapies.
Keywords: Expi293F cells; biotherapeutics; human cell line engineering; microencapsulation; site-specific transgenesis; λ integrase.
Copyright © 2023 Siddiqui, Peter, Ngoh, Wang, Ng, Dangerfield, Gunzburg, Dröge and Makhija.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors SN, JD, and WG were employed by Austrianova Singapore Pte. Ltd.; Authors HM and PD are the co-founders and shareholders of LambdaGen Pte. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A non-viral genome editing platform for site-specific insertion of large transgenes.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 Sep 3;11(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01890-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32883366 Free PMC article.
-
A novel λ integrase-mediated seamless vector transgenesis platform for therapeutic protein expression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Sep 19;46(16):e99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky500. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29893931 Free PMC article.
-
A novel Bxb1 integrase RMCE system for high fidelity site-specific integration of mAb expression cassette in CHO Cells.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2017 Aug;114(8):1837-1846. doi: 10.1002/bit.26268. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2017. PMID: 28186334
-
PITT: pronuclear injection-based targeted transgenesis, a reliable transgene expression method in mice.Exp Anim. 2012;61(5):489-502. doi: 10.1538/expanim.61.489. Exp Anim. 2012. PMID: 23095812 Review.
-
Genome-wide manipulations of Drosophila melanogaster with transposons, Flp recombinase, and ΦC31 integrase.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;859:203-28. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-603-6_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22367874 Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in mammalian display technology for therapeutic antibody development and beyond: current landscape, challenges, and future prospects.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 24;15:1469329. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1469329. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39381002 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

