Factors Associated with Tuberculosis Mortality in Manjung District, Perak, Malaysia
- PMID: 37425385
- PMCID: PMC10325130
- DOI: 10.21315/mjms2023.30.3.15
Factors Associated with Tuberculosis Mortality in Manjung District, Perak, Malaysia
Abstract
Background: Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable disease which contributes to a major cause of ill health. Worldwide, it is one of the leading causes of death from a single infectious agent.
Objectives: The study aimed to describe the epidemiology and factors associated with TB mortality in Manjung district, Perak, Malaysia.
Methods: All confirmed TB cases from 2015 to 2020 registered in Manjung district under Sistem Maklumat Tibi (MyTB) were included. Factors associated with TB mortality were analysed by using simple and multiple logistic regression analysis.
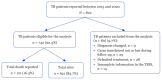
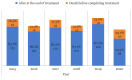
Results: A total of 742 TB cases were included in the analysis, from which 121 cases (16.3%) died before completing their treatment. The highest death was reported in 2020 (25.7%) and the lowest in 2019 (12.9%). From multiple logistic regression analysis, age 45 years old-64 years old (adjusted OR = 3.62; 95% CI: 1.38, 9.54), > 65 years old (adjusted OR = 8.67; 95% CI: 3.17, 23.74), non-Malaysian (adjusted OR = 5.18; 95% CI: 2.04, 13.14), cases notified by government hospitals (adjusted OR = 6.78; 95% CI: 3.04, 15.09), HIV-positive status (adjusted OR = 8.60; 95% CI: 3.58, 20.67) and HIV testing not offered/unknown (adjusted OR = 2.58; 95% CI: 1.18, 5.62) were significantly associated with TB mortality.
Conclusion: This study found that TB patients who were 45 years old and above, positive HIV, late diagnosis and are foreigners had a higher risk for TB mortality. Early diagnosis, optimised screening and close monitoring should be practised to reduce TB mortality.
Keywords: risk factors; tuberculosis; tuberculosis mortality.
© Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia, 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Global tuberculosis report. WHO; 2021. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240037021.
-
- Roberts CA, Davies PD, Blevins KE, Stone AC. Chapter 10. Preventable and curable, but still a global problem: tuberculosis from an evolutionary perspective. In: Plomp KA, et al., editors. Palaeopathology and evolutionary medicine: an integrated approach. Oxford University Press; 2022. pp. 179–203. - DOI
-
- Awang H, Ning GS, Ahmad MH, Mohamed KA, Zuber MFM, Embong K, et al. Epidemiology of mortality among tuberculosis patients on treatment in Terengganu state of Malaysia. J Health Trans Med. 2022;25(1):76–83. doi: 10.22452/jummec.vol25no1.13. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources