The effects of flipped classrooms to improve learning outcomes in undergraduate health professional education: A systematic review
- PMID: 37425620
- PMCID: PMC10326838
- DOI: 10.1002/cl2.1339
The effects of flipped classrooms to improve learning outcomes in undergraduate health professional education: A systematic review
Abstract
Background: The 'flipped classroom' approach is an innovative approach in educational delivery systems. In a typical flipped class model, work that is typically done as homework in the didactic model is interactively undertaken in the class with the guidance of the teacher, whereas listening to a lecture or watching course-related videos is undertaken at home. The essence of a flipped classroom is that the activities carried out during traditional class time and self-study time are reversed or 'flipped'.
Objectives: The primary objectives of this review were to assess the effectiveness of the flipped classroom intervention for undergraduate health professional students on their academic performance, and their course satisfaction.
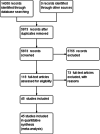
Search methods: We identified relevant studies by searching MEDLINE (Ovid), APA PsycINFO, Education Resources Information Center (ERIC) as well as several more electronic databases, registries, search engines, websites, and online directories. The last search update was performed in April 2022.
Selection criteria: Included studies had to meet the following criteria: Participants: Undergraduate health professional students, regardless of the type of healthcare streams (e.g., medicine, pharmacy), duration of the learning activity, or the country of study. Intervention: We included any educational intervention that included the flipped classroom as a teaching and learning tool in undergraduate programs, regardless of the type of healthcare streams (e.g., medicine, pharmacy). We also included studies that aimed to improve student learning and/or student satisfaction if they included the flipped classroom for undergraduate students. We excluded studies on standard lectures and subsequent tutorial formats. We also excluded studies on flipped classroom methods, which did not belong to the health professional education(HPE) sector (e.g., engineering, economics). Outcomes: The included studies used primary outcomes such as academic performance as judged by final examination grades/scores or other formal assessment methods at the immediate post-test, as well as student satisfaction with the method of learning. Study design: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs), quasi-experimental studies (QES), and two-group comparison designs. Although we had planned to include cluster-level RCTs, natural experiments, and regression discontinuity designs, these were not available. We did not include qualitative research.
Data collection and analysis: Two members of the review team independently screened the search results to assess articles for their eligibility for inclusion. The screening involved an initial screening of the title and abstracts, and subsequently, the full text of selected articles. Discrepancies between the two investigators were settled through discussion or consultation with a third author. Two members of the review team then extracted the descriptions and data from the included studies.
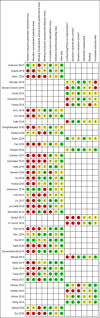
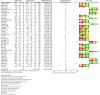
Main results: We found 5873 potentially relevant records, of which we screened 118 of them in full text, and included 45 studies (11 RCTs, 19 QES, and 15 two-group observational studies) that met the inclusion criteria. Some studies assessed more than one outcome. We included 44 studies on academic performance and eight studies on students' satisfaction outcomes in the meta-analysis. The main reasons for excluding studies were that they had not implemented a flipped class approach or the participants were not undergraduate students in health professional education. A total of 8426 undergraduate students were included in 45 studies that were identified for this analysis. The majority of the studies were conducted by students from medical schools (53.3%, 24/45), nursing schools (17.8%, 8/45), pharmacy schools (15.6%, 7/45). medical, nursing, and dentistry schools (2.2%, 1/45), and other health professional education programs (11.1%, 5/45). Among these 45 studies identified, 16 (35.6%) were conducted in the United States, six studies in China, four studies in Taiwan, three in India, two studies each in Australia and Canada, followed by nine single studies from Brazil, German, Iran, Norway, South Korea, Spain, the United Kingdom, Saudi Arabia, and Turkey. Based on overall average effect sizes, there was better academic performance in the flipped class method of learning compared to traditional class learning (standardised mean difference [SMD] = 0.57, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.25 to 0.90, τ 2: 1.16; I 2: 98%; p < 0.00001, 44 studies, n = 7813). In a sensitivity analysis that excluded eleven studies with imputed data from the original analysis of 44 studies, academic performance in the flipped class method of learning was better than traditional class learning (SMD = 0.54, 95% CI = 0.24 to 0.85, τ 2: 0.76; I 2: 97%; p < 0.00001, 33 studies, n = 5924); all being low certainty of evidence. Overall, student satisfaction with flipped class learning was positive compared to traditional class learning (SMD = 0.48, 95% CI = 0.15 to 0.82, τ 2: 0.19, I 2:89%, p < 0.00001, 8 studies n = 1696); all being low certainty of evidence.
Authors' conclusions: In this review, we aimed to find evidence of the flipped classroom intervention's effectiveness for undergraduate health professional students. We found only a few RCTs, and the risk of bias in the included non-randomised studies was high. Overall, implementing flipped classes may improve academic performance, and may support student satisfaction in undergraduate health professional programs. However, the certainty of evidence was low for both academic performance and students' satisfaction with the flipped method of learning compared to the traditional class learning. Future well-designed sufficiently powered RCTs with low risk of bias that report according to the CONSORT guidelines are needed.
© 2023 The Authors. Campbell Systematic Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Campbell Collaboration.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Recovery schools for improving behavioral and academic outcomes among students in recovery from substance use disorders: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 4;14(1):1-86. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.9. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131375 Free PMC article.
-
Small class sizes for improving student achievement in primary and secondary schools: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 11;14(1):1-107. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.10. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131395 Free PMC article.
-
School-based interventions for reducing disciplinary school exclusion: a systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 9;14(1):i-216. doi: 10.4073/csr.2018.1. eCollection 2018. Campbell Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 37131379 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted school-based interventions for improving reading and mathematics for students with or at risk of academic difficulties in Grades K-6: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 6;17(2):e1152. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1152. eCollection 2021 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 37131926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring flipped classrooms in undergraduate nursing and health science: A systematic review.Nurse Educ Pract. 2022 Oct;64:103417. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2022.103417. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Nurse Educ Pract. 2022. PMID: 36113354
Cited by
-
Developing health education to connect subject learning to real life: A pilot study for junior high school students.J Family Med Prim Care. 2025 May;14(5):1781-1787. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1540_24. Epub 2025 May 31. J Family Med Prim Care. 2025. PMID: 40547720 Free PMC article.
-
The Flipped Classroom Approach: A Review of Cognitive Styles and Academic Performances.Cureus. 2024 Jul 3;16(7):e63729. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63729. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39100016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EASL Schools of Hepatology: Pioneering the flipped classroom model and blended learning in medical education.JHEP Rep. 2024 Nov 14;7(1):101266. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2024.101266. eCollection 2025 Jan. JHEP Rep. 2024. PMID: 39872237 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of the Inverted Classroom Approach in a Case-Study Course on Antithrombotic Drug Use in a PharmD Curriculum: French Monocentric Randomized Study.JMIR Med Educ. 2025 Apr 10;11:e67419. doi: 10.2196/67419. JMIR Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40209025 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of flipped classroom method in physical education on the intrinsic motivation, self-efficacy, and learning satisfaction: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2025 May 20;20(5):e0324609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324609. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40392836 Free PMC article.
References
Anderson 2017
-
- Anderson, Jr., H. G. , Frazier, L , Anderson, S. , Stanton, R. , Gillette, C. , Broedel‐Zaugg, K. , & Yingling, K. (2017). Comparison of pharmaceutical calculations learning outcomes achieved within a traditional lecture or flipped classroom andragogy. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 81(4), Article 70. - PMC - PubMed
Angadi 2019
Baris 2020
-
- Baris, S. , & Melih, E. (2020). Using traditional or flipped classrooms to teach “vascular access skill”: A pilot study to investigate the impact of the flipped classroom approach on students' competencies. Social Science Journal, 09/18, 1–14. 10.1016/j.soscij.2019.09.002 - DOI
Bossaer 2016
Boysen‐Osborn 2016
-
- Boysen‐Osborn, M. , Anderson, C. L. , Navarro, R. , Yanuck, J. , Strom, S. , McCoy, E. , Youm, J. , Ypma‐Wong, M. F. , & Langdorf, M. I. (2016). Flipping the advanced cardiac life support classroom with team‐based learning: Comparison of cognitive testing performance for medical students at the University of California, Irvine, United States. Journal of Educational Evaluation for Health Professions, 13, 11. 10.3352/jeehp.2016.13.11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Burak 2015
-
- Burak, K. , McLaughlin, K. , Coderre, S. , Busche, K. , & Raman, M. (2015). The flipped classroom improves learning of hepatology in undergraduate medical education. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology (Australia), (Suppl. 3), 98–99.
Chaudhuri 2019
-
- Chaudhuri, A. , & Ray, B. (2019). A comparative study of outcome of flipped class room assisted lecture classes and traditional lecture classes among first MBBS students in a medical college of West Bengal. International Journal of Research and Review, 6(12), 574–580.
Cheng 2016
Chiu 2018
-
- Chiu, H. Y. , Kang, Y. N. , Wang, W. L. , Huang, H. C. , Wu, C. C. , Hsu, W. , Tong, Y.‐S. , & Wei, P.‐L. (2018). The effectiveness of a simulation‐based flipped classroom in the acquisition of laparoscopic suturing skills in medical students—A pilot study. Journal of surgical education, 75(2), 326–332. - PubMed
Chu 2019
Cotta 2016
-
- Cotta, K. I. , Shah, S. , Almgren, M. M. , Macías‐Moriarity, L. Z. , & Mody, V. (2016). Effectiveness of flipped classroom instructional model in teaching pharmaceutical calculations. Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning, 8(5), 646–653.
Dehghanzadeh 2020
-
- Dehghanzadeh, S. , Ritzenthaler, D. , Sun, A. , Rudert, N. , & Lewis, J. (2020). Comparing the effects of traditional lecture and flipped classroom on nursing students' critical thinking disposition: A quasi‐experimental study. Medical Teacher, 42(3), 285–290. - PubMed
Dodiya 2019
-
- Dodiya, D. , Vadasmiya, D. S. , & Diwan, J. (2019). A comparative study of flip classroom teaching method versus traditional classroom teaching method in undergraduate medical students in physiology. National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 9, 6.
Evans 2016
-
- Evans, K. H. , Atalie, C. , Thompson, A. C. , O'Brien, C. , Bryant, M. , Basaviah, P. , Prober, C. , & Popat, R. A. (2016). An innovative blended preclinical curriculum in clinical epidemiology and biostatistics: impact on student satisfaction and performance. Academic Medicine, 91(5), 696–700. - PubMed
Fan 2020
Gillispie 2016
Grønlien 2021
-
- Grønlien, H. K. , Christoffersen, T. E. , Ringstad, Ø. , Andreassen, M. , & Lugo, R. G. (2021). A blended learning teaching strategy strengthens the nursing students' performance and self‐reported learning outcome achievement in an anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry course—A quasi‐experimental study. Nurse Education in Practice, 52, 103046. 10.1016/j.nepr.2021.103046 - DOI - PubMed
Harrington 2015
-
- Harrington, S. A. , Bosch, M. V. , Schoofs, N. , Beel‐Bates, C. , & Anderson, K. (2015). Quantitative outcomes for nursing students in a flipped classroom. Nursing Education Perspectives, 36(3), 179–181.
Heitz 2015
Herrero 2020
Hu 2019
-
- Hu, X. , Zhang, H. , Song, Y. , Wu, C. , Yang, Q. , Shi, Z. , Zhang, X. , & Chen, W. (2019). Implementation of flipped classroom combined with problem‐based learning: An approach to promote learning about hyperthyroidism in the endocrinology internship. BMC Medical Education, 19, 290. - PMC - PubMed
Huang 2020
Isherwood 2019
-
- Isherwood, G. , Taylor, K. , Burnside, G. , Fitzgerald, R. , & Flannigan, N. (2020). Teaching orthodontic emergencies using the “flipped classroom” method of teaching-A mixed methods RCT. European Journal of Dental Education, 24(1), 53–62. - PubMed
Kuhl 2017
-
- Kuhl, S. J. , Toberer, M. , Keis, O. , Tolks, D. , Fischer, M. R. , & Kühl, M. (2017). Concept and benefits of the inverted classroom method for a competency‐based biochemistry course in the pre‐clinical stage of a human Medicine course of studies. GMS Journal for Medical Education, 34(3), 1–13. 10.3205/zma001108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lin 2017
Lucchetti 2018
-
- Lucchetti, A. L. G. , da Silva Ezequiel, O. , de Oliveira, I. N. , Moreira‐Almeida, A. , & Lucchetti, G. (2018). Using traditional or flipped classrooms to teach “geriatrics and gerontology”? Investigating the impact of active learning on medical students' competences. Medical Teacher, 40(12), 1248–1256. 10.1080/0142159X.2018.1426837 - DOI - PubMed
Missildine 2013
-
- Missildine, K. , Fountain, R. , Summers, L. , & Gosselin, K. (2013). Flipping the classroom to improve student performance and satisfaction. Journal of Nursing Education, 52(10), 597–599. - PubMed
Morton 2017
-
- Morton, D. A. , & Colbert‐Getz, J. M. (2017). Measuring the impact of the flipped anatomy classroom: The importance of categorizing an assessment by Bloom's taxonomy. Anatomical Sciences Education, 10(2), 170–175. - PubMed
O'Connor 2016
-
- O'Connor, E. E. , Fried, J. , McNulty, N. , Shah, P. , Hogg, J. P. , Lewis, P. , Zeffiro, T. , Agarwal, V. , & Reddy, S. (2016). Flipping radiology education right side up. Academic Radiology, 23(7), 810–822. - PubMed
Park 2018
-
- Park, E. O. , & Park, J. H. (2018). Quasi‐experimental study on the effectiveness of a flipped classroom for teaching adult health nursing. Japan Academy of Nursing Science, 15, 125–134. - PubMed
Ren 2020
Rui 2017
Sajid 2020
-
- Sajid, M. , Shaikh, A. , Ikram, M. , Cahusac, P. , Yaqinuddin, A. , Alkattan, W. , & Rohra, D. (2020). Comparative analysis of effectiveness between flipped classroom and Lecture‐Based classroom in undergraduate medical education at Alfaisal University. Cureus, 12(11), e11408. 10.7759/cureus.11408 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Sinclair‐Bennett 2019
-
- Sinclair‐Bennett, R. (2019). Flipped pedagogy versus traditional lecture: Examining clinical reasoning in associate degree nursing education [PhD dissertation at Capella University]. https://search.proquest.com/docview/2320958050?pq-origsite=gscholar&from...
Stewart 2013
-
- Stewart, D. W. , Panus, P. C. , & Hagemeier, N. E. (2013). An analysis of student performance with podcasting and active learning in a pharmacotherapy module. Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning, 5(6), 574–579.
Street 2015
-
- Street, S. E. , Gilliland, K. O. , McNeil, C. , & Royal, K. (2015). The flipped classroom improved medical student performance and satisfaction in a pre‐clinical physiology course. Medical Science Educator, 25(1), 35–43.
Suda 2014
-
- Suda, K. J. , Sterling, J. M. , Guirguis, A. B. , & Mathur, S. K. (2014). Student perception and academic performance after implementation blended learning approach to a drug information and literature evaluation course. Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning, 6(3), 367–372.
Tang 2017
Wang 2021
Whelan 2015
-
- Whelan, A. , Leddy, J. J. , Mindra, S. , Matthew, H. J. D. , El‐Bialy, S. , & Ramnanan, C. J. (2016). Student perceptions of independent versus facilitated small group learning approaches to compressed medical anatomy education. Anatomical Sciences Education, 9(1), 40–51. - PubMed
Whillier 2015
Wilson 2016
-
- Wilson, J. A. , Waghel, R. C. , Free, N. R. , & Borries, A. (2016). Impact of team‐based learning on perceived and actual retention of over‐the counter pharmacotherapy. Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning, 8(5), 640–645.
Wong 2014
Zheng 2020
-
- Zheng, Z. , Yuan, S. , Huang, M. , Liao, J. , Cai, R. , Zhan, H. , Yang, Z. , & Xiong, Y. (2022). Flipped classroom approach used in the training of mass casualty triage for medical undergraduate students. Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness, 16(1), 94–101. 10.1017/dmp.2020.162 - DOI - PubMed
Zhu 2020
-
- Zhu, L. , Lian, Z. , & Engstrom, M. (2020). Use of a flipped classroom in ophthalmology courses for nursing, dental and medical students: A quasi‐experimental study using a mixed‐methods approach. Nurse Education Today, 85, 104262. - PubMed
Almanase 2018
-
- Almanase, M. A. H. (2018). The impact of the flipped classroom instructional model on MPharm students in two pharmacy schools in the UK [PhD thesis]. https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/10041878/12/Almanasef_10041878_the...
Almodaires 2019
-
- Almodaires, A. A. , Alayyar, G. M. , Almsaud, T. O. , & Almutairi, F. M. (2019). The effectiveness of flipped learning: A quasi‐experimental study of the perceptions of Kuwaiti pre‐service teachers. International Education Studies, 12(1), 10–23.
Angshurekha 2020
-
- Angshurekha, D. , Purnima, B. , Atanu, C. , & Uttara, B. (2020). Introducing flipped classroom to undergraduate students in microbiology. Internal Journal of Health Research and Medico Legal Practice, 6, 1.
Appleyard 2019
-
- Appleyard, J. W. (2020). Using a flipped classroom approach in medical education: A medical student's perspective. Medical Teacher, 42(7), 839–840. - PubMed
Armbruster 2009
Belfi 2015
-
- Belfi, L. M. , Bartolotta, R. J. , Giambrone, A. E. , Davi, C. , & Min, R. J. (2015). “Flipping” the introductory clerkship in radiology: Impact on medical student performance and perceptions. Academic Radiology, 22(6), 794–801. - PubMed
Bonnes 2014
-
- Bonnes, S. L. , Ratelle, J. T. , Halvorsen, A. J. , Carter, K. J. , Hafdahl, L. T. , Wang, A. T. , Mandrekar, J. N. , Oxentenko, A. S. , Beckman, T. J. , & Wittich, C. M. (2017). Flipping the quality improvement classroom in residency education. Academic Medicine, 92, 101–107. 10.1097/ACM.0000000000001412 - DOI - PubMed
Brown 2019
-
- Brown P. (2019). A mixed method study: Assessing critical thinking, a mixed method study: Assessing critical thinking, metacognition, and motivation in a flipped classroom metacognition, and motivation in a flipped classroom instructional model [PhD thesis, The University of Southern Mississippi]. file:///C:/Users/user/Desktop/Flipped%20classroom/Brown%20(Thesis).pdf
Burak 2017
-
- Burak, K. W. , Raman, M. , Paget, M. , Busche, K. , Coderre, S. , & McLaughlin, K. (2017). A mixed methods study on the effect of flipping the undergraduate medical classroom. Education Sciences, 7(4), 83. 10.3390/educsci7040083 - DOI
Burden 2015
-
- Burden, M. L. , Carlton, K. H. , Siktberg, L. , & Pavlechko, G. (2015). Flipping the classroom strategies for psychiatric‐mental health course. Nurse Educator, 40(5), 233–236. - PubMed
Busebaia 2020
-
- Busebaia, T. J. A. , & John, B. (2020). Can flipped classroom enhance class engagement and academic performance among undergraduate pediatric nursing students? A mixed‐methods study. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 15(1), 1–16. 10.1186/s41039-020-0124-1 - DOI
Chan 2020
-
- Chan, S.‐Y. , Lamb, Y. K. , & Ng, T. F. (2020). Student's perception on initial experience of flipped classroom in pharmacy education: Are we ready? Innovations in Education and Teaching Internationa, 57(1), 62–73.
Chen 2017
-
- Chen, F. , Lui, A. M. , & Martinelli, S. M. (2017). A systematic review of the effectiveness of flipped classrooms in medical education. Medical Education, 51(6), 585–597. - PubMed
Day 2018
Ding 2019
Dombrowski 2018
El‐Banna 2017
-
- El‐Banna, M. M. , Whitlow, M. , & McNelis, A. M. (2017). Flipping around the classroom: Accelerated bachelor of science in nursing students' satisfaction and achievement. Nurse Education Today, 56, 41–46. - PubMed
Espada 2020
-
- Espada, M. , Navia, J. , Gomez, P. , & Gómez, L. M. (2020). Development of the learning to learn competence in the university context: Flipped classroom or traditional method? research in learning technology. Research in Learning Technology, 28, 2251. 10.25304/rlt.v28.2251 - DOI
Fatima 2017
Fatima 2019
Galway 2014
Geist 2015
-
- Geist, M. J. , Larimore, D. , Rawiszer, H. , & Sager, A. W. A. (2015). Flipped versus traditional instruction and achievement in a baccalaureate nursing pharmacology course. Nurse Education Perspective, 36(2), 114–115. - PubMed
Gomez‐Carrasco 2020
Hew 2018
Hongsawong 2016
-
- Hongsawong, N. (2016). Effects of four learning methods on medical students' learning outcomes in pediatrics. In AMEE. 3II16 (132308).
Hopper 2020
-
- Hopper, M. K. (2020). A collection of active learning techniques used to maximize student engagement in an advanced physiology course. Journal of the Human Anatomy and Physiology Society, 19, 3.
Hurtubise 2015
Katilya 2020
-
- Katilya, W. , & Sarah, O. W. (2020). Just‐in‐time teaching and technology to enhance student learning in lab. In Nursing Education Research Conference 2020 (Vol. 40).
Kim 2020
King 2018
Kiviniemi 2014
Koo 2016
Kugley 2016
-
- Kugley, S. , Wade, A. , Thomas, J. , Mahood, Q. , Jørgensen, A. M. K. , Hammerstrøm, K. , & Sathe, N. (2016). Searching for studies: A guide to information retrieval for Campbell systematic reviews. Campbell Methods Guides, 1, 1–81. 10.4073/cmg.2016.1 - DOI
Kuhl 2019
-
- Kuhl, S. J. , Schneider, A. , Kestler, H. A. , Toberer, M. , Kuhl, M. , & Fischer, M. R. (2019). Investigating the self‐study phase of an inverted biochemistry classroom—Collaborative dyadic learning makes the difference. BMC Medical Education, 19(1), 1–14. 10.1186/s12909-019-1497-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lew 2016
Libert 2016
-
- Liebert, C. A. , Mazer, L. , Bereknyei, M. S. , Lin, D. T. , & Lau, J. N. (2016). Student perceptions of a simulation‐based flipped classroom for the surgery clerkship: A mixed‐methods study. Surgery, 160(3), 591–598. - PubMed
Marchalot 2017
-
- Marchalot, A. , Dureuil, B. , Veber, B. , Fellahi, J. L. , Hanouz, J. L. , Dupont, H. , Lorne, E. , Gerard, J. L. , & Compère, V. (2017). Effectiveness of a blended learning course and flipped classroom in first year anaesthesia training. Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain Medicine, 37(5), 411–415. - PubMed
Martinelli 2017
-
- Martinelli, S. M. , Chen, F. , DiLorenzo, A. N. , Mayer, D. C. , Fairbanks, S. , Moran, K. , Ku, C. , Mitchell, J. D. , Bowe, E. A. , Royal, K. D. , Hendrickse, A. , VanDyke, K. , Trawicki, M. C. , Rankin, D. , Guldan, G. J. , Hand, W. , Gallagher, C. , Jacob, Z. , Zvara, D. A. , … Schell, R. M. (2017). Results of a flipped classroom teaching approach in anesthesiology residents. Journal of Graduate Medical Education, 9(4), 485–490. - PMC - PubMed
McLaughlin 2013
-
- McLaughlin, J. E. , Griffin, L. M. , Esserman, D. A. , Davidson, C. A. , Glatt, D. M. , Roth, M. T. , Gharkholonarehe, N. , & Mumper, R. J. (2013). Pharmacy student engagement, performance, and perception in a flipped satellite classroom. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 77(9), 196. - PMC - PubMed
McLaughlin 2014
-
- McLaughlin, J. E. , Roth, M. T. , Glatt, D. M. , Gharkholonarehe, N. , Davidson, C. A. , Griffin, L. M. , Esserman, D. A. , & Mumper, R. J. (2014). The flipped classroom: A course redesign to foster learning and engagement in a health professions school. Academic Medicine, 4(89), 236–243. - PubMed
Moraros 2015
Njie‐Carr 2017
Oliv́an 2019
-
- Oliv́an, B. B. , Masluk, B. , Gascon, S. , Fueyo, D. R. , Aguilar‐Latorre, A. , Artola, M. I. , & Botaya, R. M. (2019). The use of flipped class room as an active learning approach improves academic performance in social work: A randomized trial in a university. PLoS ONE, 14(4), e0214623. - PMC - PubMed
Oudbier 2022
Park 2015
-
- Park, S. E. , & Howell, T. H. (2015). Implementation of a flipped classroom educational model in a predoctoral dental course. Journal of Dental Education, 79(5), 563–570. - PubMed
Pierce 2012
Piercea 2012
Porcaro 2016
-
- Porcaro, P. A. , Jackson, D. E. , McLaughlin, P. M. , & O'Malley, C. J. (2016). Curriculum design of a flipped classroom to enhance haematology learning. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 25(3), 345–357.
Ramnanan 2017
Rao 2001
-
- Rao, S. P. , & DiCarlo, S. E. (2001). Active learning of respiratory physiology improves performance on respiratory physiology examinations. Advanced Physiology Education, 25(1–4), 127–133. - PubMed
Rehman 2020
Riddle 2017
Roig‐Vila 2019
-
- Roig‐Vila, R. , & Herrero, J. F. A. (2019). Impact on Twitter of active methodologies PBL, flipped classroom and gamification. Revista Iberoamericana de Educación a Distancia, 22(2), 79–96.
Roy 2020
-
- Roy, H. , Ray, K. , Saha, S. , & Ghosal, A. (2020). A study on students' perceptions for online Zoom‐app based flipped class sessions on anatomy organised during the lock down period of COVID‐19. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 14(6), 1–4. 10.7860/JCDR/2020/44869.13797 - DOI
Sait 2017
Sandrone 2020
-
- Sandrone, S. , Berthaud, J. V. , Carlson, C. , Cios, J. , Dixit, N. , Farheen, A. , Kraker, J. , Owens, J. W. M. , Patino, G. , Sarva, H. , Weber, D. , & Schneider, L. D. (2020). Strategic considerations for applying the flipped classroom to neurology education. Annals of Neurology, 87(1), 4–9. - PubMed
Sathapornsathid 2016
-
- Sathapornsathid, A. (2016). Flipped classroom and its effectiveness compared with traditional‐style lecture in stroke rehabilitation medicine course for medical students: Randomized controlled trials. In AMEE. 31114(133617).
Schlairet 2014
-
- Schlairet, M. C. , Green, R. , & Benton, M. J. (2014). The flipped classroom for an undergraduate nursing course. Nurse Educator, 39(6), 321–325. - PubMed
Schneider 2019
Sheppard 2017
-
- Sheppard, M. E. , Vitalone‐Raccaro, N. , Kaari, J. M. , & Ajumobi, T. T. (2017). Using a flipped classroom and the perspective of families to teach medical students about children with disabilities and special education. Disability and Health Journal, 10(4), 552–558. - PubMed
Smith 2017
-
- Smith, C. E. (2017). The flipped classroom benefits of student‐led learning. Nursing, 47(4), 20–22. - PubMed
Sohn 2019
Tsang 2016
Tune 2013
-
- Tune, J. D. , Sturek, M. , & Basile, D. P. (2013). Flipped classroom model improves graduate student performance in cardiovascular, respiratory, and renal physiology. Advances in Physiology Education, 37(4), 316–320. - PubMed
Vadakedath 2019
Vavasseur 2020
-
- Vavasseur, A. , Muscari, F. , Meyrignac, O. , Nodot, M. , Dedouit, F. , Revel‐Mouroz, P. , Dercle, L. , Rozenblum, L. , Wang, L. , Maulat, C. , Rousseau, H. , Otal, P. , Dercle, L. , & Mokrane, F.‐Z. (2020). Blended learning of radiology improves medical students' performance, satisfaction, and engagement. Insights into Imaging, 11(1), 61. - PMC - PubMed
Veeramani 2015
Wang 2020
-
- Wang, X. , Dong, L. , Lyu, W. , & Geng, Z. (2020). Teaching health assessment symptomatology using a flipped classroom combined with scenario simulation. Journal of Nursing Education, 59(8), 448–452. - PubMed
Watson 2015
Wozny 2018
-
- Wozny, N. , Balser, C. , & Ives, D. (2018). Evaluating the flipped classroom: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Economic Education, 49(2), 115–129.
Wu 2018
Wu 2020
-
- Wu, S. , Pan, S. , Ren, Y. , Yu, H. , Chen, Q. , Liu, Z. , & Guo, Q. (2020). Existing contradictions and suggestions: Flipped classroom in radiology courses of musculoskeletal disease under Chinese medical educational mode from medical imaging student perspective. BMC Medical Education, 20(1), 75. - PMC - PubMed
Young 2014
Al Faris 2013
-
- Al Faris, E. A. , Naeem, N. , McAleer, S. , Qureshi, R. , Van der Vleuten, C. , Irfan, F. , & Jamal, A. (2013). Why a teacher centred medical school curriculum May result in a poor educational environment. Medical Education, 2(2), 85–90.
Atkins 2004
-
- Atkins, D. , Eccles, M. , Flottorp, S. , Guyatt, G. H. , Henry, D. , Hill, S. , Liberati, A. , O'Connell, D. , Oxman, A. D. , Phillips, B. , Schünemann, H. , Edejer, T. T. , Vist, G. E. , Williams, J. W. , & GRADE Working Group . (2004). Systems for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations I: Critical appraisal of existing approaches. BMC Health Services Research, 4, 38. - PMC - PubMed
Baker 2000
-
- Baker, J. T. (2000). The “classroom flip”: Using web course management tools to become the guide on the side. In 11th International Conference on College Teaching and Learning.
Bergmann 2012
-
- Bergmann, J. , Overmyer, J. , & Wilie, B. (2012). The daily riff—Be smarter. About Education. http://www.thedailyriff.com/articles/the-flipped-class-conversation-689.php
Betihavas 2016
-
- Betihavas, V. , Bridgman, H. , Kornhaber, R. , & Cross, M. (2016). The evidence for ‘flipping out’: A systematic review of the flipped classroom in nursing education. Nurse Education Today, 38, 15–21. - PubMed
Bishop 2013
-
- Bishop, J. L. , & Verleger, M. A. (2013). The flipped classroom: A survey of the research. In Proceedings of the ASEE Annual Conference.
Bligh 2000
-
- Bligh, D. A. (2000). What's the use of lectures?. Jossey‐Bass.
Borenstein 2009
-
- Borenstein, M. , Hedges, L. V. , Higgins, J. P. T. , & Rothstein, H. R. (2009). Introduction to meta‐analysis. Meta‐Regression (Chapter 20; pp. 187–203). Chichester, UK: Wiley.
David 1989
-
- Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13, 319–339.
Deeks 2020
-
- Deeks, J. J. , Higgins, J. P. T. , & Altman, D. G. (Eds). (2020). Chapter 10: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In J. P. T. Higgins, J. Thomas, J. Chandler, M. Cumpston, T. Li, M. J. Page, & V. A. Welch (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). Cochrane. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Dietrichson 2021
-
- Dietrichson, J. , Filges, T. , Seerup, J. K. , Klokker, R. H. , Viinholt, B. C. , Bøg, M. , & Eiberg, M. (2021). Targeted school‐based interventions for improving reading and mathematics for students with or at risk of academic difficulties in grades K‐6: A systematic review. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 17(2), e1152. 10.1002/cl2.1152 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ellis 2010
-
- Ellis, P. D. (2010). Part 1. Effect sizes and the interpretation of results. In The essential guide to effect sizes: Statistical power, meta‐analysis, and the interpretation of research results (pp. 1–4). Cambridge University Press.
EPOC 2009
-
- Effective Practice and Organization of Care (EPOC) . (2009). Risk of bias tool. https://epoc.cochrane.org/epoc-author-resources
EPOC 2017b
-
- EPOC . (2017). Suggested risk of bias criteria for EPOC reviews. Cochrane Effective Practice and Organisation of Care (EPOC). EPOC Resources for review authors. https://epoc.cochrane.org/resources/epoc-resources-review-authors
Freeman 2014
-
- Freeman, S. , Eddy, S. L. , McDonough, M. , Smith, M. K. , Okoroafor, N. , Jordt, H. , & Wenderoth, M. P. (2014). Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111, 8410–8415. - PMC - PubMed
Fulton 2012
-
- Fulton, K. (2012). Upside down and inside out: Flip your classroom to improve student learning. Learning and Leading With Technology, 39, 12–17. http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ982840.pdf
Gillette 2018
Gross 2015
Hamdan 2013
-
- Hamdan, N. , McKnight, P. , McKnight, K. , & Arfstorm, K. M. (2013). A review of flipped learning. Flipped Learning Network, George Mason University: Harper and Row Ltd. www.flippedlearning.org/cms/lib07/VA01923112/Centricity/Domain/41/LitReview
Hedges 2007
-
- Hedges, L. , & Hedberg, E. C. (2007). Intraclass correlations for planning group randomized experiments in rural education. Journal of Research in Rural Education, 22, 10.
Hedges 2010
Herreid 2013
-
- Herreid, C. F. , & Schiller, N. A. (2013). Case studies and the flipped classroom. Journal of College Science Teaching, 42(5), 62–66.
Hew 2018
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins, J. P. T. , Savović, J. , Page, M. J. , Elbers, R. G. , & Sterne, J. A. C. (2011). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In Higgins J. P. T., Thomas J., Chandler J., Cumpston M., Li T., Page M. J., & Welch V. A. (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). Cochrane. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Higgins 2020
-
- Higgins, J. P. T. , Eldridge, S. , & Li, T. (2020). Chapter 23: Including variants on randomized trials. In J. P. T. Higgins, J. Thomas, J. Chandler, M. Cumpston, T. Li, M. J. Page, & V. A. Welch (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.1 (updated September). Cochrane. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Issenberg 2005
-
- Issenberg, S. B. , McGaghie, W. C. , Petrusa, E. R. , Lee Gordon, D. , & Scalese, R. J. (2005). Features and uses of high‐fidelity medical simulations that lead to effective learning: A BEME systematic review. Medical Teacher, 27(1), 10–28. - PubMed
Johnson 2013
-
- Johnson, G. B. (2013). Student perceptions of the flipped classroom [Unpublished master's thesis, University of British Columbia].
Johnson 2016
-
- Johnson, L. , Becker, S. A. , Cummins, M. , Estrada, V. , Freeman, A. , & Hall, C. (2016). NMC horizon report. Higher Education Edition. The New Media Consortium.
Kachka 2012
-
- Kachka, P. (2012). Understanding the flipped classroom: Part 2. Faculty Focus.
King 1993
-
- King, A. (1993). From sage on the stage to guide on the side. College Teaching, 41(1), 30–35.
Kirkpatrick 2006
-
- Kirkpatrick, D. , & Kirkpatrick, J. (2006). Evaluating training programs: The four levels. Berrett‐Koehler.
Lag 2019
-
- Låg, T. , & Sæle, R. G. (2019). Does the flipped classroom improve student learning and satisfaction? A systematic review and meta‐analysis. AERA Open, 5, 3. 10.1177/2332858419870489 - DOI
Lage 2000
-
- Lage, M. J. , Platt, G. J. , & Treglia, M. (2000). Inverting the classroom: A gateway to creating an inclusive learning environment. The Journal of Economic Education, 31(1), 30. 10.2307/1183338 - DOI
Luo 2018
Mccoy 2015
-
- McCoy, L. , Pettit, R. K. , Lewis, J. H. , Bennett, T. , Carrasco, N. , Brysacz, S. , Makin, I. R. S. , Hutman, R. , & Schwartz, F. N. (2015). Developing technology‐enhanced active learning for medical education: Challenges, solutions, and future directions. Journal of the American Osteopathic Association, 115(4), 202–211. - PubMed
Moffett 2015
-
- Moffett, J. (2015). Twelve tips for “flipping” the classroom. Medical Teacher, 37(4), 331–336. - PubMed
Morrison 2014
-
- Morrison, C. D. (2014). From ‘sage on the stage’ to ‘guide on the side’: A good start. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 8, 1. 10.20429/ijsotl.2014.080104 - DOI
Musallam 2011
-
- Musallam, R. (2011). Should you flip your classroom. https://www.edutopia.org/blog/flipped-classroom-ramsey-musallam
Persky 2017
Prober 2013
-
- Prober, C. G. , & Khan, S. (2013). Medical education reimagined: A call to action. Academic Medicine, 88, 1407–1410. - PubMed
Revman Web 2019
-
- The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager Web (RevManWeb) . Version 1.22.0 [Computer program]. (2019). The Cochrane Collaboration. revman.cochrane.org
Rohwer 2017
-
- Rohwer, A. , Motaze, N. V. , Rehfuess, E. , & Young, T. (2017). E‐learning of evidence‐based health care (EBHC) to increase EBHC competencies in healthcare professionals: A systematic review. The Campbell Collaboration, 4. 10.4073/csr.2017.4 - DOI
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann, H. J. , Higgins, J. P. T. , Vist, G. E. , Glasziou, P. , Akl, E. A. , Skoetz, N. , & Guyatt, G. H. (2020). Chapter 14: Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence. In Higgins J. P. T., Thomas J., Chandler J., Cumpston M., Li T., Page M. J., & Welch V. A. (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020). Cochrane. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook
Schünemann 2022
-
- Schünemann, H. J. , Vist, G. E. , Higgins, J. P. , Santesso, N. , Deeks, J. J. , Glasziou, P. , & Ekl, E. A. (2022). Chapter 15: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In Higgins J. P., Thomas J., Chandler J., Cumpston M. S., Li T., & Page M. J., et al. (Eds.), Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.3 (updated February 2022). Cochrane. training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Staker 2012
-
- Staker, H. , & Horn, M. B. (2012). Classifying K‐12 blended learning. Innosight Institute.
Tetreault 2013
-
- Tetreault, P. L. (2013). The flipped classroom: Cultivating student engagement. A project submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of master education in the Department of Curriculum and Instruction. University of Victoria.
Van Vliet 2015
Venkatesh 2003
-
- Venkatesh, V. , Morris, M. G. , Davis, G. B. , & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27(3), 425–478T.
Wan 2014
Naing 2019
-
- Naing, C. , Kumar Chellappan, D. , Wong Shew, F. , Riegelman, A. , & Whittaker, M. (2019). The effects of flipped classrooms to improve learning outcomes in undergraduate health professional education: A systematic review. Campbell Systematic Reviews. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 15(3), e1041. 10.1002/cl2.1041 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
