High-Fat and High-Sucrose Diet Leads to Skeletal Muscle Loss and Bladder Dysfunction in Rat
- PMID: 37425652
- PMCID: PMC10327923
- DOI: 10.2147/RRU.S406808
High-Fat and High-Sucrose Diet Leads to Skeletal Muscle Loss and Bladder Dysfunction in Rat
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, we investigated skeletal muscle loss and bladder dysfunction caused by high-fat/high-sucrose (HFS) diet.
Methods: Twelve-week-old Sprague-Dawley (SD) female rats were fed on normal (Group N) or HFS (Group HFS) diet for 12 weeks. We conducted urodynamic investigation and pharmacologic in vitro. In addition, we measured gastrocnemius and tibialis muscle weight and protein concentration. The hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in the bladder were assayed.
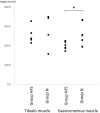
Results: The urodynamic investigations revealed the significantly shorter intercontraction intervals and lower maximal voiding pressure in Group HFS than in Group N. Furthermore, the absolute and relative weights of the gastrocnemius muscle were found to be significantly lower in Group HFS than in Group N. The protein concentration of the gastrocnemius muscle was also significantly lower in Group HFS than in Group N. The absolute and relative weights of the bladder were also significantly lower in Group HFS than in Group N. The contractile responses of the bladder strips to electrical field stimulation and carbachol were significantly lower in Group HFS than in Group N. The HIF1α and 8OHdG in the bladder muscle were significantly higher in Group HFS than in Group N. The HFS diet reduced bladder capacity and contractility along with the loss of the gastrocnemius muscle.
Conclusion: HFS diet promotes bladder dysfunction similar to detrusor hyperreflexia with impaired contractility.
Keywords: bladder dysfunction; high-fat; high-sucrose; rat; skeletal muscle.
© 2023 Wada et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors do not have any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Alterations in skeletal muscle morphology and mechanics in juvenile male Sprague Dawley rats exposed to a high-fat high-sucrose diet.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 25;13(1):12013. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38487-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37491416 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased EDHF-mediated relaxation is a major mechanism in endothelial dysfunction in resistance arteries in aged mice on prolonged high-fat sucrose diet.Physiol Rep. 2017 Dec;5(23):e13502. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13502. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29212858 Free PMC article.
-
A maternal high-fat, high-sucrose diet alters insulin sensitivity and expression of insulin signalling and lipid metabolism genes and proteins in male rat offspring: effect of folic acid supplementation.Br J Nutr. 2017 Oct;118(8):580-588. doi: 10.1017/S0007114517002501. Br J Nutr. 2017. PMID: 29056104
-
Normal detrusor is more sensitive than hypertrophied detrusor to in vitro ischemia followed by re-oxygenation.Neurourol Urodyn. 2000;19(6):701-12. doi: 10.1002/1520-6777(2000)19:6<701::aid-nau8>3.0.co;2-w. Neurourol Urodyn. 2000. PMID: 11071701
-
High Fat With High Sucrose Diet Leads to Obesity and Induces Myodegeneration.Front Physiol. 2018 Sep 5;9:1054. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01054. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30258366 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Underactive bladder as defined by the International Continence Society in the 2023 Japan Community Health Survey.Int J Urol. 2025 Jan;32(1):51-59. doi: 10.1111/iju.15595. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Int J Urol. 2025. PMID: 39382059 Free PMC article.
-
Screening tool for sarcopenia (SARC-F) predicts unsatisfactory medical treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in elderly men aged 75 years or older: a preliminary observational study.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Feb;57(2):399-406. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04233-z. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39417965
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

