This is a preprint.
Reprogramming human B cells with custom heavy chain antibodies
- PMID: 37425794
- PMCID: PMC10327003
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.28.546944
Reprogramming human B cells with custom heavy chain antibodies
Update in
-
Reprogramming human B cells with custom heavy-chain antibodies.Nat Biomed Eng. 2024 Dec;8(12):1700-1714. doi: 10.1038/s41551-024-01240-4. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Nat Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 39039240
Abstract
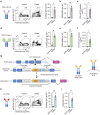
We describe a genome editing strategy to reprogram the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) locus of human B cells to express custom molecules that respond to immunization. These heavy chain antibodies (HCAbs) comprise a custom antigen-recognition domain linked to an Fc domain derived from the IgH locus and can be differentially spliced to express either B cell receptor (BCR) or secreted antibody isoforms. The HCAb editing platform is highly flexible, supporting antigen-binding domains based on both antibody and non-antibody components, and also allowing alterations in the Fc domain. Using HIV Env protein as a model antigen, we show that B cells edited to express anti-Env HCAbs support the regulated expression of both BCRs and antibodies, and respond to Env antigen in a tonsil organoid model of immunization. In this way, human B cells can be reprogrammed to produce customized therapeutic molecules with the potential for in vivo amplification.
Figures



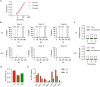
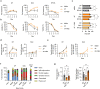
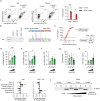

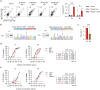



References
-
- Carter P.J. & Rajpal A. Designing antibodies as therapeutics. Cell 185, 2789–2805 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
