This is a preprint.
High density SNP array and reanalysis of genome sequencing uncovers CNVs associated with neurodevelopmental disorders in KOLF2.1J iPSCs
- PMID: 37425875
- PMCID: PMC10327134
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.26.546614
High density SNP array and reanalysis of genome sequencing uncovers CNVs associated with neurodevelopmental disorders in KOLF2.1J iPSCs
Update in
-
KOLF2.1J iPSCs carry CNVs associated with neurodevelopmental disorders.Cell Stem Cell. 2024 Mar 7;31(3):288-289. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2024.02.007. Cell Stem Cell. 2024. PMID: 38458176 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
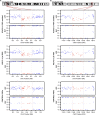
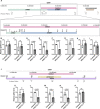
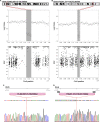
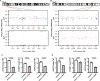
The KOLF2.1J iPSC line was recently proposed as a reference iPSC to promote the standardization of research studies in the stem cell field. Due to overall good performance differentiating to neural cell lineages, high gene editing efficiency, and absence of genetic variants associated to neurological disorders KOLF2.1J iPSC line was particularly recommended for neurodegenerative disease modeling. However, our work uncovers that KOLF2.1J hPSCs carry heterozygous small copy number variants (CNVs) that cause DTNBP1, JARID2 and ASTN2 haploinsufficiencies, all of which are associated with neurological disorders. We further determine that these CNVs arose in vitro over the course of KOLF2.1J iPSC generation from a healthy donor-derived KOLF2 iPSC line and affect the expression of DNTBP1, JARID2 and ASTN2 proteins in KOLF2.1J iPSCs and neural progenitors. Therefore, our study suggests that KOLF2.1J iPSCs carry genetic variants that may be deleterious for neural cell lineages. This data is essential for a careful interpretation of neural cell studies derived from KOLF2.1J iPSCs and highlights the need for a catalogue of iPSC lines that includes a comprehensive genome characterization analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Large structural variants in KOLF2.1J are unlikely to compromise neurological disease modelling.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 29:2024.01.29.577739. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.29.577739. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Stem Cell. 2024 Mar 7;31(3):290-291. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2024.02.006. PMID: 38352495 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Mitochondrial DNA integrity and metabolome profile are preserved in the human induced pluripotent stem cell reference line KOLF2.1J.Stem Cell Reports. 2024 Mar 12;19(3):343-350. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.01.009. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Stem Cell Reports. 2024. PMID: 38402620 Free PMC article.
-
KOLF2.1J iPSCs carry CNVs associated with neurodevelopmental disorders.Cell Stem Cell. 2024 Mar 7;31(3):288-289. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2024.02.007. Cell Stem Cell. 2024. PMID: 38458176 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reverse engineering human neurodegenerative disease using pluripotent stem cell technology.Brain Res. 2016 May 1;1638(Pt A):30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.09.023. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26423934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age Is Relative-Impact of Donor Age on Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cell Functionality.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Jan 25;5:4. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00004. eCollection 2018. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29423397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dimos J.T., Rodolfa K.T., Niakan K.K., Weisenthal L.M., Mitsumoto H., Chung W., Croft G.F., Saphier G., Leibel R., Goland R., et al. (2008). Induced pluripotent stem cells generated from patients with ALS can be differentiated into motor neurons. Science 321, 1218–1221. 10.1126/science.1158799. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
