This is a preprint.
Limited effects of dehydration on object discrimination in the novel object recognition paradigm in young and middle-aged male and female rats
- PMID: 37425948
- PMCID: PMC10327120
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.28.546884
Limited effects of dehydration on object discrimination in the novel object recognition paradigm in young and middle-aged male and female rats
Abstract
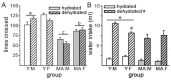
Dehydration is associated with impaired cognitive function in humans. Limited animal research also suggests that disruptions in fluid homeostasis impair performance in cognitive tasks. We previously demonstrated that extracellular dehydration impaired performance in the novel object recognition memory test in a sex and gonadal hormone specific manner. The experiments in this report were designed to further characterize the behavioral effects of dehydration on cognitive function in male and female rats. In Experiment 1, we tested whether dehydration during the training trial in the novel object recognition paradigm would impact performance, while euhydrated, in the test trial. Regardless of hydration status during training, all groups spent more time investigating the novel object during the test trial. In Experiment 2, we tested whether aging exacerbated dehydration-induced impairments on test trial performance. Although aged animals spent less time investigating the objects and had reduced activity levels, all groups spent more time investigating the novel object, compared to the original object, during the test trial. Aged animals also had reduced water intake after water deprivation and, unlike the young adult rats, there was no sex difference in water intake. Together these results, in combination with our previous findings, suggest that disruptions in fluid homeostasis have limited effects on performance in the novel object recognition test and may only impact performance after specific types of fluid manipulations.
Keywords: aging; memory; sex differences; water deprivation.
Figures



References
-
- Cian C., et al. Effects of fluid ingestion on cognitive function after heat stress or exercise-induced dehydration. Int J Psychophysiol, 2001. 42(3): p. 243–51. - PubMed
-
- Gopinathan P.M., Pichan G., and Sharma V.M., Role of dehydration in heat stress-induced variations in mental performance. Arch Environ Health, 1988. 43(1): p. 15–7. - PubMed
-
- Sharma V.M., et al. Influence of heat-stress induced dehydration on mental functions. Ergonomics, 1986. 29(6): p. 791–9. - PubMed
-
- Stachenfeld N.S., et al. Water intake reverses dehydration associated impaired executive function in healthy young women. Physiol Behav, 2018. 185: p. 103–111. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
