A guide for developing comprehensive systems biology maps of disease mechanisms: planning, construction and maintenance
- PMID: 37426048
- PMCID: PMC10325725
- DOI: 10.3389/fbinf.2023.1197310
A guide for developing comprehensive systems biology maps of disease mechanisms: planning, construction and maintenance
Abstract
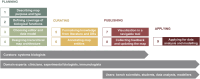
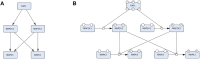
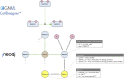
As a conceptual model of disease mechanisms, a disease map integrates available knowledge and is applied for data interpretation, predictions and hypothesis generation. It is possible to model disease mechanisms on different levels of granularity and adjust the approach to the goals of a particular project. This rich environment together with requirements for high-quality network reconstruction makes it challenging for new curators and groups to be quickly introduced to the development methods. In this review, we offer a step-by-step guide for developing a disease map within its mainstream pipeline that involves using the CellDesigner tool for creating and editing diagrams and the MINERVA Platform for online visualisation and exploration. We also describe how the Neo4j graph database environment can be used for managing and querying efficiently such a resource. For assessing the interoperability and reproducibility we apply FAIR principles.
Keywords: curation; disease mechanisms; pathway biology; systems biology; translational research.
Copyright © 2023 Mazein, Acencio, Balaur, Rougny, Welter, Niarakis, Ramirez Ardila, Dogrusoz, Gawron, Satagopam, Gu, Kremer, Schneider and Ostaszewski.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors DR and AK were employed by company ITTM Information Technology for Translational Medicine. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

