Isoproterenol pre-treatment improve the therapeutic efficacy of cardiosphere-derived cells transplantation for myocardial infarction
- PMID: 37426146
- PMCID: PMC10323591
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-22-1593
Isoproterenol pre-treatment improve the therapeutic efficacy of cardiosphere-derived cells transplantation for myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the effect of isoproterenol pre-treatment on the therapeutic efficacy of cardiosphere-derived cells (CDCs) transplantation for myocardial infarction (MI).
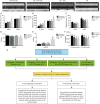
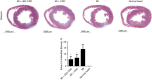
Methods: Thirty 8-week-old male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat model of MI was generated by ligation of the left anterior descending artery. The MI rats were treated with PBS (MI group, n=8), CDCs (MI + CDC group, n=8) and isoproterenol pre-treated CDCs (MI + ISO-CDC group, n=8), respectively. In the MI + ISO-CDC group, CDCs were pre-treated by 10-6 M isoproterenol and the cultured for additional 72 h, then injected to the myocardial infraction area like other groups. At 3 weeks after the operation, echocardiographic, hemodynamic, histological assessments and Western blot were performed to compare the CDCs differentiation degree and therapeutic effect.
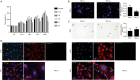
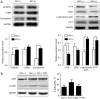
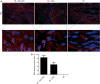
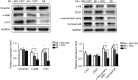
Results: Isoproterenol treatment (10-6 M) simultaneously inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis of CDCs, up-regulated proteins of vimentin, cTnT, α-sarcomeric actin and connexin 43, and down-regulated c-Kit proteins (all P<0.05). The echocardiographic and hemodynamic analysis demonstrated that the MI rats in the two CDCs transplantation groups had significantly better recovery of cardiac function than the MI group (all P<0.05). MI + ISO-CDC group had better recovery of cardiac function than the MI + CDC group, although the differences did not reach significant. Immunofluorescence staining showed that the MI + ISO-CDC group had more EdU-positive (proliferating) cells and cardiomyocytes in the infarct area than the MI + CDC group. MI + ISO-CDC group had significantly higher protein levels of c-Kit, CD31, cTnT, α-sarcomeric actin and α-SMA in the infarct area than the MI + CDC group.
Conclusions: These results suggested that in CDCs transplantation, isoproterenol pre-treated CDCs can provide a better protective effect against MI than the untreated CDCs.
Keywords: Myocardial infarction (MI); cardiosphere-derived cells (CDCs); cell transplantation; isoproterenol.
2023 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-22-1593/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metformin promotes the survival of transplanted cardiosphere-derived cells thereby enhancing their therapeutic effect against myocardial infarction.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Jan 28;8(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0476-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28129786 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac resynchronization by cardiosphere-derived stem cell transplantation in an experimental model of myocardial infarction.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011 Jul;24(7):808-14. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2011.03.003. Epub 2011 Apr 20. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011. PMID: 21511432 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of platelet gel spiked with cardiosphere-derived cells boosts structural and functional benefits relative to gel transplantation alone in rats with myocardial infarction.Biomaterials. 2012 Apr;33(10):2872-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.12.040. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Biomaterials. 2012. PMID: 22243801 Free PMC article.
-
Widespread intracoronary allogeneic cardiosphere-derived cell therapy with and without cyclosporine in reperfused myocardial infarction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Nov 1;323(5):H904-H916. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00373.2022. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36083793 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac and systemic rejuvenation after cardiosphere-derived cell therapy in senescent rats.Eur Heart J. 2017 Oct 14;38(39):2957-2967. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx454. Eur Heart J. 2017. PMID: 29020403 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
