Long-Term and Stable Dental Therapies via an In Situ Spontaneous Medicine Delivery System
- PMID: 37426210
- PMCID: PMC10324093
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02428
Long-Term and Stable Dental Therapies via an In Situ Spontaneous Medicine Delivery System
Abstract
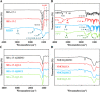
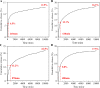
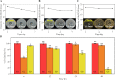
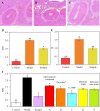
Chronic oral diseases are boring, long-term, and discomfort intense diseases, which endanger the physical and mental health of patients constantly. Traditional therapeutic methods based on medicines (including swallowing drugs, applying ointment, or injection in situ) bring much inconvenience and discomfort. A new method possessing accurate, long-term, stable, convenient, and comfortable features is in great need. In this study, we demonstrated a development of one spontaneous administration for the prevention and therapy on a series of oral diseases. By uniting dental resin and medicine-loaded mesoporous molecular sieve, nanoporous medical composite resin (NMCR) was synthesized by a simple physical mixing and light curing method. Physicochemical investigations of XRD, SEM, TEM, UV-vis, N2 adsorption, and biochemical experiments of antibacterial and pharmacodynamic evaluation on periodontitis treatment of SD rats were carried on to characterize an NMCR spontaneous medicine delivery system. Compared to existing pharmacotherapy and in situ treatments, NMCR can keep a quite long time of stable in situ medicine release during the whole therapeutic period. Taking the periodontitis treatment as an instance, the probing pocket depth value in a half-treatment time of 0.69 from NMCR@MINO was much lower than that of 1.34 from the present commercial Periocline ointment, showing an over two times effect.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long-term postoperative treatment of open fractures using in situ medicine delivery based on mesoporous MCM-41/hydrogel composites.RSC Adv. 2025 May 9;15(19):15266-15275. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00313j. eCollection 2025 May 6. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40352383 Free PMC article.
-
[A clinical study of Periocline on the treatment of severe chronic periodontitis].Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2005 Jun;14(3):257-9. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2005. PMID: 15995772 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
An injectable in situ hexagonal mesophase system for local delivery of minocycline hydrochloride: Preparation and pharmacodynamics in rats.Pharmazie. 2017 May 1;72(5):249-256. doi: 10.1691/ph.2017.6190. Pharmazie. 2017. PMID: 29441868
-
A comprehensive and critical review of dental implant prognosis in periodontally compromised partially edentulous patients.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007 Dec;18(6):669-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2007.01406.x. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007. PMID: 17868376 Review.
-
Nonsurgical periodontal therapy.Periodontol 2000. 2001;25:77-88. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0757.2001.22250106.x. Periodontol 2000. 2001. PMID: 11155183 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

