Immunological factors in cirrhosis diseases from a bibliometric point of view
- PMID: 37426317
- PMCID: PMC10324529
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i24.3899
Immunological factors in cirrhosis diseases from a bibliometric point of view
Abstract
Background: Cirrhosis results from persistent liver injury that leads to liver fibrosis. Immunological factors play important regulatory roles in the development and progression of cirrhosis. Bibliometrics is one of the most commonly used methods for systematic evaluation of a field of study. To date, there are no bibliometric studies on the role of immunological factors in cirrhosis.
Aim: To provide a comprehensive overview of the knowledge structure and research hotspots of immunological factors in cirrhosis.
Methods: We retrieved publications related to immunological factors in cirrhosis between 2003 to 2022 from the Web of Science Core Collection database on December 7, 2022. The search strategy was TS = ((Liver Cirrhosis OR hepatic cirrhosis OR liver fibrosis) AND (Immunologic* Factor* OR Immune Factor* OR Immunomodulator* OR Biological Response Modifier* OR Biomodulator*)). Only original articles and reviews were included. A total of 2873 publications were analyzed using indicators of publication and citation metrics, countries, institutes, authors, journals, references, and keywords by CiteSpace and VOSviewer.
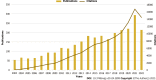
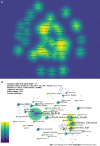
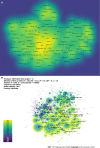
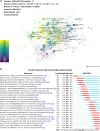
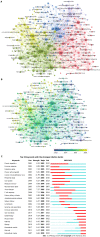
Results: A total of 5104 authors from 1173 institutions across 51 countries published 2873 papers on cirrhosis and immunological factors in 281 journals. In the past 20 years, the increasing number of related annual publications and citations indicates that research on immunological factors in cirrhosis has become the focus of attention and has entered a period of accelerated development. The United States (781/27.18%), China (538/18.73%), and Germany (300/10.44%) were the leading countries in this field. Most of the top 10 authors were from the United States (4) and Germany (3), with Gershwin ME contributing the most related articles (42). World Journal of Gastroenterology was the most productive journal, whereas Hepatology was the most co-cited journal. Current research hotspots regarding immunological factors in cirrhosis include fibrosis, cirrhosis, inflammation, liver fibrosis, expression, hepatocellular carcinoma, activation, primary biliary cirrhosis, disease, and hepatic stellate cells. Burst keywords (e.g., epidemiology, gut microbiota, and pathways) represent research frontiers that have attracted the interest of researchers in recent years.
Conclusion: This bibliometric study comprehensively summarizes the research developments and directions of immunological factors in cirrhosis, providing new ideas for promoting scientific research and clinical applications.
Keywords: Bibliometrics; Cirrhosis; CiteSpace; Immunological factors; VOSviewer; Visualization.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

