Disclosure of HIV status and adherence to antiretroviral treatment in children and adolescents from Lomé and Abidjan
- PMID: 37426461
- PMCID: PMC10323812
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2023.45.13.26795
Disclosure of HIV status and adherence to antiretroviral treatment in children and adolescents from Lomé and Abidjan
Abstract
Introduction: in Africa, the proportion of minors with AIDS is ever increasing and adherence to treatment protocols is still suboptimal. The study investigated the conditions of HIV status disclosure and adherence to treatment in patients < 19 in two West African cities.
Methods: in 2016, thirteen health professionals and four parents filled out questionnaires to identify problems and solutions relative to disclosure of HIV status and adherence to treatment in 208 children and adolescents seen at University Hospitals in Abidjan (Ivory Coast) and Lomé (Togo).
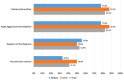
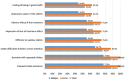
Results: medians (extrema) of patients´ ages at start and end of status disclosure process were 10 (8-13) and 15 (13-17.5) years. In 61% of cases, disclosure was made individually after preparation sessions. The main difficulties were: parents´ disapproval, skipped visits, and rarity of psychologists. The solutions proposed were: recruiting more full-time psychologists, improving personnel training, and promoting patients´ "clubs". One out of three respondents was not satisfied with patients´ adherence to treatments. The major reasons were: intake frequencies, frequent omissions, school constraints, adverse effects, and lack of perceived effect. Nevertheless, 94% of the respondents confirmed the existence of support groups, interviews with psychologists, and home visits. To improve adherence, the respondents proposed increasing the number of support groups, sustaining reminder phone calls and home visits, and supporting therapeutic mentoring.
Conclusion: despite persisting disclosure and adherence problems, appropriate measures already put into practice still need to be taken further, especially through engaging psychologists, training counsellors, and promoting therapeutic support groups.
Keywords: Children; Ivory Coast; Togo; adolescents; aids; patient compliance; truth disclosure; university hospitals.
Copyright: Tchaa Abalo Bakai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS UNAIDS. UNICEF and WHO urge countries in western and central Africa to step up the pace in the response to HIV for children and adolescents. 2019. Accessed April 2020.
-
- ONUSIDA . 2014. Tous inclus: mettre fin à l´épidémie chez les adolescents. Accessed on April 2020.
-
- Menon A, Glazebrook C, Campain N, Ngoma M. Mental health and disclosure of HIV status in Zambian adolescents with HIV infection: implications for peer-support programs. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007 Nov 1;46(3):349–54. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical