IGF-1 Therapy Improves Muscle Size and Function in Experimental Peripheral Arterial Disease
- PMID: 37426532
- PMCID: PMC10322901
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.12.006
IGF-1 Therapy Improves Muscle Size and Function in Experimental Peripheral Arterial Disease
Abstract
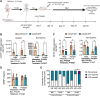
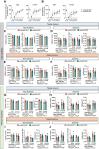
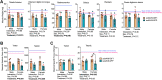
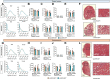
Lower-extremity peripheral arterial disease (PAD) has increased in prevalence, yet therapeutic development has remained stagnant. Skeletal muscle health and function has been strongly linked to quality of life and medical outcomes in patients with PAD. Using a rodent model of PAD, this study demonstrates that treatment of the ischemic limb with insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1 significantly increases muscle size and strength without improving limb hemodynamics. Interestingly, the effect size of IGF1 therapy was larger in female mice than in male mice, highlighting the need to carefully examine sex-dependent effects in experimental PAD therapies.
Keywords: chronic limb threatening ischemia; gene therapy; regeneration; skeletal muscle.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant R01-HL149704 (to Dr Ryan). Dr Kim was supported by American Heart Association grant POST903198. Mr Thome was supported by NIH grant F31-DK128920. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Walking Exercise Therapy Effects on Lower Extremity Skeletal Muscle in Peripheral Artery Disease.Circ Res. 2021 Jun 11;128(12):1851-1867. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318242. Epub 2021 Jun 10. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 34110902 Review.
-
Stenting for peripheral artery disease of the lower extremities: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(18):1-88. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074395 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroquine improves the response to ischemic muscle injury and increases HMGB1 after arterial ligation.J Vasc Surg. 2018 Mar;67(3):910-921. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.01.021. Epub 2017 Mar 1. J Vasc Surg. 2018. PMID: 28259568 Free PMC article.
-
Lower-extremity muscle wasting in patients with peripheral arterial disease: quantitative measurement and evaluation with CT.Eur Radiol. 2023 Jun;33(6):4063-4072. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09356-4. Epub 2022 Dec 29. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36580096
-
Skeletal muscle metabolism as a target for drug therapy in peripheral arterial disease.Vasc Med. 1996;1(1):55-9. doi: 10.1177/1358863X9600100110. Vasc Med. 1996. PMID: 9546916 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Muscle Exacerbates Ischemic Pathology in Chronic Kidney Disease.Circ Res. 2023 Jul 7;133(2):158-176. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322875. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Circ Res. 2023. PMID: 37325935 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse Skeletal Muscle Adaptations in Individuals Born Preterm-A Comprehensive Review.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 May 10;46(5):4551-4564. doi: 10.3390/cimb46050276. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38785544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in endothelial cells improves ischemic angiogenesis in chronic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Jan 1;326(1):H44-H60. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00530.2023. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 37921663 Free PMC article.
-
Gene therapy for genetic diseases: challenges and future directions.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 13;6(2):e70091. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70091. eCollection 2025 Feb. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 39949979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A 6-Minute Limb Function Assessment for Therapeutic Testing in Experimental Peripheral Artery Disease Models.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024 Oct 23;10(1):88-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2024.08.011. eCollection 2025 Jan. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39906594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conte S.M., Vale P.R. Peripheral arterial disease. Heart Lung Circ. 2018;27:427–432. - PubMed
-
- Fowkes F.G., Rudan D., Rudan I., et al. Comparison of global estimates of prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2000 and 2010: a systematic review and analysis. Lancet. 2013;382:1329–1340. - PubMed
-
- Novo S., Coppola G., Milio G. Critical limb ischemia: definition and natural history. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2004;4:219–225. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

