γδ T cells in immunotherapies for B-cell malignancies
- PMID: 37426670
- PMCID: PMC10325712
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1200003
γδ T cells in immunotherapies for B-cell malignancies
Abstract
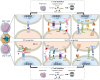
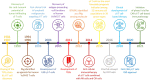
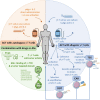
Despite the advancements in therapy for B cell malignancies and the increase in long-term survival of patients, almost half of them lead to relapse. Combinations of chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies such as anti-CD20 leads to mixed outcomes. Recent developments in immune cell-based therapies are showing many encouraging results. γδ T cells, with their potential of functional plasticity and their anti-tumoral properties, emerged as good candidates for cancer immunotherapies. The representation and the diversity of γδ T cells in tissues and in the blood, in physiological conditions or in B-cell malignancies such as B cell lymphoma, chronic lymphoblastic leukemia or multiple myeloma, provides the possibility to manipulate them with immunotherapeutic approaches for these patients. In this review, we summarized several strategies based on the activation and tumor-targeting of γδ T cells, optimization of expansion protocols, and development of gene-modified γδ T cells, using combinations of antibodies and therapeutic drugs and adoptive cell therapy with autologous or allogenic γδ T cells following potential genetic modifications.
Keywords: immunotherapy; leukemia; lymphoma; myeloma; γδ T cells.
Copyright © 2023 Rimailho, Faria, Domagala, Laurent, Bezombes and Poupot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anti-tumor cytotoxicity of gammadelta T cells expanded from peripheral blood cells of patients with myeloma and lymphoma.Med Oncol. 2008;25(2):137-47. doi: 10.1007/s12032-007-9004-4. Epub 2007 Sep 11. Med Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18488155
-
γδ T-cell immunotherapy for lung cancer.Surg Today. 2011 May;41(5):606-11. doi: 10.1007/s00595-010-4478-7. Epub 2011 May 1. Surg Today. 2011. PMID: 21533930 Review.
-
Gammadelta T cells for immune therapy of patients with lymphoid malignancies.Blood. 2003 Jul 1;102(1):200-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3665. Epub 2003 Mar 6. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12623838 Clinical Trial.
-
Haploidentical γδ T Cells Induce Complete Remission in Chemorefractory B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.J Immunother. 2023 Feb-Mar 01;46(2):56-58. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000450. Epub 2023 Jan 10. J Immunother. 2023. PMID: 36723414 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting B Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA) in Multiple Myeloma: Potential Uses of BCMA-Based Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 10;9:1821. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01821. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30147690 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Gamma Delta T Lymphocytes in Physiological and Pathological Condition-Focus on Psoriasis, Atopic Dermatitis, Autoimmune Disorders, Cancer and Lymphomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 21;25(14):7960. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147960. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063202 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in adoptive cellular immunotherapy and therapeutic breakthroughs in multiple myeloma.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024 Oct 28;13(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s40164-024-00576-6. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39468695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The capability of heterogeneous γδ T cells in cancer treatment.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 24;14:1285801. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1285801. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38077392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gamma delta T cells in cancer therapy: from tumor recognition to novel treatments.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 19;11:1480191. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1480191. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39748921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vδ2 T-cell engagers bivalent for Vδ2-TCR binding provide anti-tumor immunity and support robust Vγ9Vδ2 T-cell expansion.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 18;14:1474007. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1474007. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39493452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deusch K, Lüling F, Reich K, Classen M, Wagner H, Pfeffer K. A major fraction of human intraepithelial lymphocytes simultaneously expresses the γ/δ T cell receptor, the CD8 accessory molecule and preferentially uses the Vδ1 gene segment. Eur J Immunol (1991) 21:1053–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210429 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

