Enhancing zinc levels in Solanum lycopersicum L. through biofortification with plant growth-promoting Pseudomonas spp. isolated from cow dung
- PMID: 37427026
- PMCID: PMC10323744
- DOI: 10.5114/bta.2023.127205
Enhancing zinc levels in Solanum lycopersicum L. through biofortification with plant growth-promoting Pseudomonas spp. isolated from cow dung
Abstract
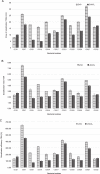
Zinc is a vital micronutrient for all life forms, and Zn-solubilizing bacteria (ZSB) present in the soil convert inorganic zinc into forms available for plants. This study assessed ZSB isolated from cow dung for their plant growth-promoting (PGP) characteristics and potential to enhance tomato plant growth. The experiment assayed a total of 30 bacteria from cow dung for Zn-solubilization using insoluble ZnO and ZnCO3. Atomic absorption spectroscopy quantitatively evaluated Zn-solubilization, and the isolates were further studied for Zn-solubilization and plant growth in Solanum lycopersicum. The CDS7 and CDS27 isolates were the most significant Zn-solubilizing strains. CDS7 exhibited increased ZnO solubility (32.1 mg/l) compared to CDS21 (23.7 mg/l). PGP trait quantitative results revealed that the CDS7 and CDS21 bacterial strains solubilized insoluble phosphate (287.2 and 217.7 μg/ml, respectively) and produced indole acetic acid (22.1 and 14.8 μg/ml, respectively). Based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing, CDS7 and CDS21 were identified as Pseudomonas kilonensis and Pseudomonas chlororaphis, and 16S rDNA sequences were submitted to the GenBank database. Furthermore, ZSB strains were administered to tomato seeds under a pot study. The treatments with CDS7 inoculant and a consortium of both isolates were reported with maximum plant development (stem length 63.16 and 59.89 cm, respectively) and zinc content (3.13 and 2.36 mg/100 g, respectively) in tomato fruit compared to the control. In conclusion, microorganisms isolated from cow dung with PGP activity can improve Zn bioavailability and plant growth sustainably. They can be used as biofertilizers in agricultural fields to improve plant growth and production.
Keywords: Pseudomonas; Solanum lycopersicum; biofortification; plant growth promotion; zinc.
© 2023 Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Polish Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed R., Yusoff Abd Samad M., Uddin M., Quddus M., Hossain M.A. (2021) Recent trends in the foliar spraying of zinc nutrient and zinc oxide nanoparticles in tomato production. Agronomy 11(10): 2074.
-
- Baliyan N., Dheeman S., Maheshwari D.K., Dubey R.C., Vishnoi V.K. (2018) Rhizobacteria isolated under field first strategy improved chickpea growth and productivity. Environ. Sustain. 1(4): 461–469.
-
- Baruah N., Mondal S.C., Farooq M., Ogoi G.N. (2019) Influence of heavy metals on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat, pea, and tomato. Water Air Soil Pollut. 230(12): 1–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
