Clinical outcome of established diagnostic and treatment modalities of COVID-19-associated myocarditis: a systematic review
- PMID: 37427189
- PMCID: PMC10328593
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000964
Clinical outcome of established diagnostic and treatment modalities of COVID-19-associated myocarditis: a systematic review
Abstract
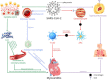
Despite the significant research and development of COVID-19 diagnostic and therapeutic approaches, the virus still poses a concern, particularly to groups that are already vulnerable. Several individuals experienced cardiac problems like myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, and pericarditis after they had recovered from the infection. Early diagnosis and timely management of sequelae are part of the therapy. However, there are gaps in the knowledge of the diagnostic and definitive treatment options for COVID-19 myocarditis. This review focuses on myocarditis associated with COVID-19.
Objective: This systemic review provides the most recent overview of myocarditis caused by COVID-19, including clinical manifestations, diagnostic techniques, available treatments, and outcomes.
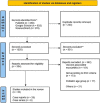
Methods: The PubMed, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect servers were used to conduct a systematic search in compliance with the PRISMA guidelines. Boolean search terms included "(COVID-19)" OR "(COVID19)" OR "(COVID-19 VIRUS INFECTION)" AND "(MYOCARDITIS)". The results were tabulated and analyzed.
Results: A total of 32 studies, including 26 case reports and 6 case series, were included in the final analysis, and 38 cases of COVID-19-associated myocarditis were analyzed. Middle-aged men constituted the most affected population (60.52%). Dyspnoea (63.15%), chest pain or discomfort (44.73%), and fever (42.10%) were the prevalent presentations. ST-segment abnormalities were reported in 48.38% of cases on electrocardiography testing. Leucocytic infiltration (60%) was the frequent finding obtained on endomyocardial biopsy. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging yielded myocardial oedema (63.63%), and late gadolinium enhancement (54.54%) as the most common findings. Reduced ejection fraction (75%) was the frequent result obtained on echocardiography. Corticosteroids (76.31%) and immunomodulators (42.10%) were the well-established in-hospital medications. Veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (35%) was the most common intervention used to support the treatment. The frequent in-hospital complications were cardiogenic shock (30.76%), followed by pneumonia (23.07%). The mortality rate was 7.9%.
Conclusion: Early detection and timely management of myocarditis are essential to reduce the risk of developing further complications. It is crucial to emphasize the need to evaluate COVID-19 as a possible cause of myocarditis in populations that are young and healthy to avoid fatal consequences.
Keywords: COVID-19; cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; echocardiography; endomyocardial biopsy; myocarditis; steroids.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 Infection and Myocarditis: A State-of-the-Art Systematic Review.J Prim Care Community Health. 2021 Jan-Dec;12:21501327211056800. doi: 10.1177/21501327211056800. J Prim Care Community Health. 2021. PMID: 34854348 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of case reports on COVID-19 associated myocarditis: a discussion on treatments.Virol J. 2024 Oct 9;21(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02499-4. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39385302 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Involvement in COVID-19 Patients: A Contemporary Review.Infect Dis Rep. 2021 Jun 1;13(2):494-517. doi: 10.3390/idr13020048. Infect Dis Rep. 2021. PMID: 34206074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fulminant Myocarditis and Cardiogenic Shock Following COVID-19 Infection Versus COVID-19 Vaccination: A Systematic Literature Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 25;12(5):1849. doi: 10.3390/jcm12051849. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36902636 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 fulminant myocarditis recovered with veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and Impella CP.J Cardiol Cases. 2023 May 10;28(3):116-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jccase.2023.05.003. Online ahead of print. J Cardiol Cases. 2023. PMID: 37361643 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Echocardiographic Assessment in Patients Recovered from Acute COVID-19 Illness.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Aug 15;10(8):349. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10080349. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37623362 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection.Adv Surg. 2024 Sep;58(1):249-273. doi: 10.1016/j.yasu.2024.05.003. Epub 2024 Jun 29. Adv Surg. 2024. PMID: 39089781 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
