Kangfuxin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats by inhibiting NF-κB p65 activation and regulating T lymphocyte subsets
- PMID: 37427322
- PMCID: PMC10329251
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.68771.14990
Kangfuxin alleviates ulcerative colitis in rats by inhibiting NF-κB p65 activation and regulating T lymphocyte subsets
Abstract
Objectives: Ulcerative colitis (UC) remains an enduring, idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease marked by persistent mucosal inflammation initiating from the rectum and extending in a proximal direction. An ethanol extract of Periplaneta americana L., namely Kangfuxin (KFX), has a significant historical presence in Traditional Chinese Medicine and has been broadly utilized in clinical practice for the treatment of injury. Here, we aimed to determine the effect of KFX on 2,4,6-trinitro'benzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced UC in Sprague-Dawley rats.
Materials and methods: We established the UC model by TNBS/ethanol method. Then, the rats were subject to KFX (50, 100, 200 mg/kg/day) for 2 weeks by intragastric gavage. The body weight, disease activity index (DAI), colonic mucosal injury index (CMDI), and histopathological score were evaluated. The colonic tissue interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-10, transforming growth factor-1 (TGF-β1), and epidermal growth factor (EGF) were determined by Elisa. To study T-lymphocyte subsets, flow cytometry was performed. In addition, the expression level of NF-κB p65 was evaluated by immunohistochemistry and western blot analysis.
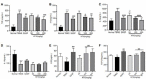
Results: Compared with the TNBS-triggered colitis rats, the treatment of rats with KFX significantly increased the body weight, and decreased DAI, CMDI, and histopathological score. Also, KFX elicited a reduction in the secretion of colonic pro-inflammatory cytokines, namely IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, concomitant with up-regulation of IL-10, TGF-β1, and EGF levels. Upon KFX treatment, the CD3+CD4+/CD3+CD8+ ratio in the spleen decreased, while the CD3+CD8+ subset and the CD3+CD4+CD25+/CD3+CD4+ ratio demonstrated an increase. In addition, the expression of NF-κB p65 in the colon was decreased.
Conclusion: KFX effectively suppresses TNBS-induced colitis by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB p65 and regulating the ratio of CD4+/CD8+.
Keywords: Inflammation mediators; Inflammatory bowel disease; Kangfuxin; T lymphocyte subsets; Ulcerative colitis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The ethanol extract of Periplaneta Americana L. improves ulcerative colitis induced by a combination of chronic stress and TNBS in rats.Acta Cir Bras. 2022 Aug 12;37(5):e370505. doi: 10.1590/acb370505. eCollection 2022. Acta Cir Bras. 2022. PMID: 35976342 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Sishen Wan on dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced ulcerative colitis and its effect on toll-like receptor 2/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4/nuclear factor-κB signal pathway.J Tradit Chin Med. 2022 Aug;42(4):565-575. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20220608.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 35848973 Free PMC article.
-
[Electroacupuncture of "Shangjuxu"(ST37) and "Tianshu"(ST25) reduces colonic injury by suppressing NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling in rats with ulcerative colitis].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Apr 25;47(4):314-20. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210361. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 35486010 Chinese.
-
Temperature-sensitive hydrogel for rectal perfusion improved the therapeutic effect of Kangfuxin liquid on DSS-induced ulcerative colitis mice: The inflammation alleviation and the colonic mucosal barriers repair.Int J Pharm. 2020 Nov 15;589:119846. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119846. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32891717
-
Therapeutic effect of Patrinia villosa on TNBS-induced ulcerative colitis via metabolism, vitamin D receptor and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Apr 24;288:114989. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.114989. Epub 2022 Jan 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35032589
Cited by
-
Inosine, AMP, and Vidarabine: Network Pharmacology and LC-MS Reveal Key Bioactive Compounds in Periplaneta americana for Ulcerative Colitis Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 6;26(12):5446. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125446. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564909 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ordás I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 2012;380:1606–1619. - PubMed
-
- Eftychi C, Schwarzer R, Vlantis K, Wachsmuth L, Basic M, Wagle P, et al. Temporally distinct functions of the cytokines IL-12 and IL-23 drive chronic colon inflammation in response to intestinal barrier impairment. Immunity. 2019;51:367–380. - PubMed
-
- Maloy KJ, Powrie F. Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2011;474:298–306. - PubMed
-
- Neurath MF. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:329–342. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
