Propolis and its constituents against cardiovascular risk factors including obesity, hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes, and dyslipidemia: A comprehensive review
- PMID: 37427329
- PMCID: PMC10329244
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2023.67793.14835
Propolis and its constituents against cardiovascular risk factors including obesity, hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes, and dyslipidemia: A comprehensive review
Abstract
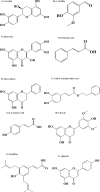
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are some of the major causes of death worldwide. The modern lifestyle elevates the risk of CVDs. CVDs have several risk factors such as obesity, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes. Using herbal and natural products plays a pivotal role in the treatment of different diseases such as CVDs, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Propolis, a natural resinous mixture, is made by honey bees. Its main components are phenolics and terpenoid compounds such as caffeic acid phenethyl ester, chrysin, and quercetin. In this review, multiple studies regarding the pharmacological impacts of propolis and its constituents with their related mechanisms of action against mentioned CVD risk factors have been discussed in detail. Here, we used electronic databases or search engines such as Scopus, Web of Science, Pubmed, and Google Scholar without time limitations. The primary components of propolis are phenolics and terpenoid compounds such as caffeic acid phenethyl ester, chrysin and quercetin. Propolis and its constituents have been found to exhibit anti-obesity, anti-hypertension, anti-dyslipidemic, anti-atherosclerosis, and anti-diabetic effects. The vast majority of studies discussed in this review demonstrate that propolis and its constituents could have therapeutic effects against mentioned CVD risk factors via several mechanisms such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, reducing adipogenesis, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory effect, inhibition of the ACE, increasing insulin secretion, NO level, etc.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease Diabetes; Dyslipidemia; Hypertension; Obesity; Propolis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Propolis in the management of cardiovascular disease.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;266(Pt 2):131219. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131219. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38556227 Review.
-
Fatty Acid Analysis, Chemical Constituents, Biological Activity and Pesticide Residues Screening in Jordanian Propolis.Molecules. 2021 Aug 21;26(16):5076. doi: 10.3390/molecules26165076. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443664 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Role of Propolis in the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Diseases.Plants (Basel). 2021 Apr 27;10(5):883. doi: 10.3390/plants10050883. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33925692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Propolis: Its Role and Efficacy in Human Health and Diseases.Molecules. 2022 Sep 19;27(18):6120. doi: 10.3390/molecules27186120. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of potential inhibitor properties of ethanolic propolis extracts against ACE-II receptors for COVID-19 treatment by molecular docking study.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Aug;203(6):3557-3564. doi: 10.1007/s00203-021-02351-1. Epub 2021 May 5. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33950349 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Propolis Consumption on Body Composition and Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2024 Jul 25;101:100754. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2024.100754. eCollection 2024. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2024. PMID: 39247130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the role of VLDL in the relationship between type 2 diabetes and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendelian randomization analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Oct 30;10:1234271. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1234271. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37965087 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary antioxidants and hypertension among menopausal women in Rafsanjan Cohort Study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 3;14(1):12703. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63401-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38830913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lordan R, Tsoupras A, Zabetakis I. Platelet activation and prothrombotic mediators at the nexus of inflammation and atherosclerosis: Potential role of antiplatelet agents. Blood Rev. 2020;45:100694. - PubMed
-
- Canto ED, Ceriello A, Ryde L, Ferrini M, Hansen TB, Schnell O, et al. Diabetes as a cardiovascular risk factor: An overview of global trends of macro and micro vascular complications Diabetes cardiovascular risk. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019;26:25–32. - PubMed
-
- Lavie CJ, Milani R V, Ventura HO. Obesity and cardiovascular disease Risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53:1925–1932. - PubMed
-
- Kokubo Y, Matsumoto C. Hypertension is a risk factor for several types of heart disease: Review of prospective studies. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:419–426. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous