A membrane protein of the rice pathogen Burkholderia glumae required for oxalic acid secretion and quorum sensing
- PMID: 37428013
- PMCID: PMC10576180
- DOI: 10.1111/mpp.13376
A membrane protein of the rice pathogen Burkholderia glumae required for oxalic acid secretion and quorum sensing
Abstract
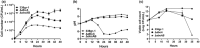
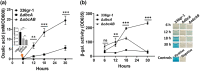
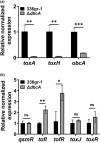
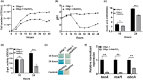
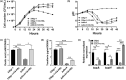
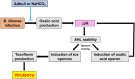
Bacterial panicle blight is caused by Burkholderia glumae and results in damage to rice crops worldwide. Virulence of B. glumae requires quorum sensing (QS)-dependent synthesis and export of toxoflavin, responsible for much of the damage to rice. The DedA family is a conserved membrane protein family found in all bacterial species. B. glumae possesses a member of the DedA family, named DbcA, which we previously showed is required for toxoflavin secretion and virulence in a rice model of infection. B. glumae secretes oxalic acid as a "common good" in a QS-dependent manner to combat toxic alkalinization of the growth medium during the stationary phase. Here, we show that B. glumae ΔdbcA fails to secrete oxalic acid, leading to alkaline toxicity and sensitivity to divalent cations, suggesting a role for DbcA in oxalic acid secretion. B. glumae ΔdbcA accumulated less acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) QS signalling molecules as the bacteria entered the stationary phase, probably due to nonenzymatic inactivation of AHL at alkaline pH. Transcription of toxoflavin and oxalic acid operons was down-regulated in ΔdbcA. Alteration of the proton motive force with sodium bicarbonate also reduced oxalic acid secretion and expression of QS-dependent genes. Overall, the data show that DbcA is required for oxalic acid secretion in a proton motive force-dependent manner, which is critical for QS of B. glumae. Moreover, this study supports the idea that sodium bicarbonate may serve as a chemical for treatment of bacterial panicle blight.
Keywords: bacterial panicle blight; oxalic acid; pH homeostasis; quorum sensing.
© 2023 The Authors. Molecular Plant Pathology published by British Society for Plant Pathology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
qsmR encoding an IclR-family transcriptional factor is a core pathogenic determinant of Burkholderia glumae beyond the acyl-homoserine lactone-mediated quorum-sensing system.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Oct 3;20(10):e1011862. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011862. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39361719 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical or Genetic Alteration of Proton Motive Force Results in Loss of Virulence of Burkholderia glumae, the Cause of Rice Bacterial Panicle Blight.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Aug 26;87(18):e0091521. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00915-21. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34260305 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential genetic components involved in the deviant quorum-sensing signaling pathways of Burkholderia glumae through a functional genomics approach.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Mar 10;5:22. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00022. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25806356 Free PMC article.
-
Burkholderia glumae: next major pathogen of rice?Mol Plant Pathol. 2011 May;12(4):329-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00676.x. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Mol Plant Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21453428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of bacterial metabolism by quorum sensing.Trends Microbiol. 2015 Sep;23(9):567-76. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2015.05.007. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Trends Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26072043 Review.
Cited by
-
qsmR encoding an IclR-family transcriptional factor is a core pathogenic determinant of Burkholderia glumae beyond the acyl-homoserine lactone-mediated quorum-sensing system.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Oct 3;20(10):e1011862. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011862. eCollection 2024 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39361719 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal Effects of Pulsed-Light Treatment Against Burkholderia gladioli pv. cocovenenans in Auricularia: Mechanisms and Influences.Foods. 2025 Jun 25;14(13):2246. doi: 10.3390/foods14132246. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40647000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barton, I.S. , Eagan, J.L. , Nieves‐Otero, P.A. , Reynolds, I.P. , Platt, T.G. & Fuqua, C. (2021) Co‐dependent and interdigitated: dual quorum sensing systems regulate conjugative transfer of the Ti plasmid and the At megaplasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens 15955. Frontiers in Microbiology, 11, 605896. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cardona, S.T. & Valvano, M.A.J.P. (2005) An expression vector containing a rhamnose‐inducible promoter provides tightly regulated gene expression in Burkholderia cenocepacia . Plamsid, 54, 219–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

