Ceftolozane-Tazobactam against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cystic Fibrosis Clinical Isolates in the Hollow-Fiber Infection Model: Challenges Imposed by Hypermutability and Heteroresistance
- PMID: 37428034
- PMCID: PMC10433881
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00414-23
Ceftolozane-Tazobactam against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cystic Fibrosis Clinical Isolates in the Hollow-Fiber Infection Model: Challenges Imposed by Hypermutability and Heteroresistance
Abstract
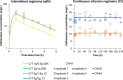
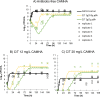
Pseudomonas aeruginosa remains a challenge in chronic respiratory infections in cystic fibrosis (CF). Ceftolozane-tazobactam has not yet been evaluated against multidrug-resistant hypermutable P. aeruginosa isolates in the hollow-fiber infection model (HFIM). Isolates CW41, CW35, and CW44 (ceftolozane-tazobactam MICs of 4, 4, and 2 mg/L, respectively) from adults with CF were exposed to simulated representative epithelial lining fluid pharmacokinetics of ceftolozane-tazobactam in the HFIM. Regimens were continuous infusion (CI; 4.5 g/day to 9 g/day, all isolates) and 1-h infusions (1.5 g every 8 hours and 3 g every 8 hours, CW41). Whole-genome sequencing and mechanism-based modeling were performed for CW41. CW41 (in four of five biological replicates) and CW44 harbored preexisting resistant subpopulations; CW35 did not. For replicates 1 to 4 of CW41 and CW44, 9 g/day CI decreased bacterial counts to <3 log10 CFU/mL for 24 to 48 h, followed by regrowth and resistance amplification. Replicate 5 of CW41 had no preexisting subpopulations and was suppressed below ~3 log10 CFU/mL for 120 h by 9 g/day CI, followed by resistant regrowth. Both CI regimens reduced CW35 bacterial counts to <1 log10 CFU/mL by 120 h without regrowth. These results corresponded with the presence or absence of preexisting resistant subpopulations and resistance-associated mutations at baseline. Mutations in ampC, algO, and mexY were identified following CW41 exposure to ceftolozane-tazobactam at 167 to 215 h. Mechanism-based modeling well described total and resistant bacterial counts. The findings highlight the impact of heteroresistance and baseline mutations on the effect of ceftolozane-tazobactam and limitations of MIC to predict bacterial outcomes. The resistance amplification in two of three isolates supports current guidelines that ceftolozane-tazobactam should be utilized together with another antibiotic against P. aeruginosa in CF.
Keywords: dynamic in vitro model; mechanism-based modeling; pharmacodynamics; whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Meropenem Combined with Ciprofloxacin Combats Hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Respiratory Infections of Cystic Fibrosis Patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Oct 24;62(11):e01150-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01150-18. Print 2018 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30104278 Free PMC article.
-
Ceftolozane/tazobactam plus tobramycin against free-floating and biofilm bacteria of hypermutable Pseudomonas aeruginosa epidemic strains: Resistance mechanisms and synergistic activity.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2023 Sep;62(3):106887. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2023.106887. Epub 2023 Jun 12. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2023. PMID: 37315906
-
Comparison of Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Infusion Regimens in a Hollow-Fiber Infection Model against Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0089222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00892-22. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35695526 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa ST235 in cystic fibrosis.Paediatr Respir Rev. 2018 Jun;27:18-20. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2018.05.009. Epub 2018 May 18. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2018. PMID: 29914746 Review.
-
Use of continuous-infusion ceftolozane/tazobactam for resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections: a retrospective analysis and brief review of the literature.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020 Nov;56(5):106158. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106158. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020. PMID: 32919007 Review.
Cited by
-
A freely accessible, adaptable hollow-fiber setup to reproduce first-order absorption: illustration with linezolid cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetic data.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jun 3;13(6):e0005125. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00051-25. Epub 2025 May 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40372038 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying and mathematically modeling the time-course of extracellular metabolic markers associated with resistance to ceftolozane/tazobactam in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Apr 3;68(4):e0108123. doi: 10.1128/aac.01081-23. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38376189 Free PMC article.
-
Ceftolozane/tazobactam disrupts Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms under static and dynamic conditions.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025 Feb 3;80(2):372-380. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkae413. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2025. PMID: 39657684 Free PMC article.
-
Lytic transglycosylase Slt of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a periplasmic hub protein.Protein Sci. 2024 Jul;33(7):e5038. doi: 10.1002/pro.5038. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38864725 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutational resistome dynamics using an enrichment panel for direct sequencing of clinical samples.EBioMedicine. 2024 Oct;108:105367. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105367. Epub 2024 Sep 26. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39332391 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. 2022. Cystic fibrosis foundation patient registry 2021 annual data report. https://www.cff.org/sites/default/files/2021-11/Patient-Registry-Annual-.... Accessed 26 March 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

