Machine Learning-Assisted Recurrence Prediction for Patients With Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 37428988
- PMCID: PMC10569772
- DOI: 10.1200/CCI.22.00062
Machine Learning-Assisted Recurrence Prediction for Patients With Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Stratifying patients with cancer according to risk of relapse can personalize their care. In this work, we provide an answer to the following research question: How to use machine learning to estimate probability of relapse in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC)?
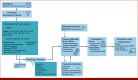
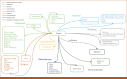
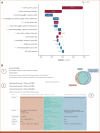
Materials and methods: For predicting relapse in 1,387 patients with early-stage (I-II) NSCLC from the Spanish Lung Cancer Group data (average age 65.7 years, female 24.8%, male 75.2%), we train tabular and graph machine learning models. We generate automatic explanations for the predictions of such models. For models trained on tabular data, we adopt SHapley Additive exPlanations local explanations to gauge how each patient feature contributes to the predicted outcome. We explain graph machine learning predictions with an example-based method that highlights influential past patients.
Results: Machine learning models trained on tabular data exhibit a 76% accuracy for the random forest model at predicting relapse evaluated with a 10-fold cross-validation (the model was trained 10 times with different independent sets of patients in test, train, and validation sets, and the reported metrics are averaged over these 10 test sets). Graph machine learning reaches 68% accuracy over a held-out test set of 200 patients, calibrated on a held-out set of 100 patients.
Conclusion: Our results show that machine learning models trained on tabular and graph data can enable objective, personalized, and reproducible prediction of relapse and, therefore, disease outcome in patients with early-stage NSCLC. With further prospective and multisite validation, and additional radiological and molecular data, this prognostic model could potentially serve as a predictive decision support tool for deciding the use of adjuvant treatments in early-stage lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. : Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209-249, 2021 - PubMed
-
- Cancer of the lung and bronchus—Cancer stat Ffacts. SEER. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html
-
- CLARIFY Project. https://www.clarify2020.eu/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

