Targeting the Androgen Signaling Axis in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 37429011
- PMCID: PMC10852396
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.00433
Targeting the Androgen Signaling Axis in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
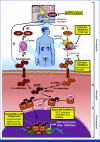
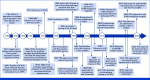
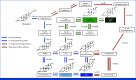
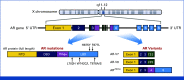
Activation of the androgen receptor (AR) and AR-driven transcriptional programs is central to the pathophysiology of prostate cancer. Despite successful translational efforts in targeting AR, therapeutic resistance often occurs as a result of molecular alterations in the androgen signaling axis. The efficacy of next-generation AR-directed therapies for castration-resistant prostate cancer has provided crucial clinical validation for the continued dependence on AR signaling and introduced a range of new treatment options for men with both castration-resistant and castration-sensitive disease. Despite this, however, metastatic prostate cancer largely remains an incurable disease, highlighting the need to better understand the diverse mechanisms by which tumors thwart AR-directed therapies, which may inform new therapeutic avenues. In this review, we revisit concepts in AR signaling and current understandings of AR signaling-dependent resistance mechanisms as well as the next frontier of AR targeting in prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures
References
-
- Wilson JD, George FW, Griffin JE. The hormonal control of sexual development. Science. 1981;211:1278–1284. - PubMed
-
- Quigley CA, De Bellis A, Marschke KB, et al. Androgen receptor defects: Historical, clinical, and molecular perspectives. Endocr Rev. 1995;16:271–321. - PubMed
-
- Huggins C, Hodges CV. Studies on prostatic cancer I The effect of castration, of estrogen and of androgen Injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. Cancer Res. 1941;1:293–297. - PubMed
-
- Huggins C, Stevens RE, Hodges CV. Studies on prostatic cancer: II The effects of castration on advanced carcinoma of the prostate gland. Arch Surg. 1941;43:209–223.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

