Pyroptosis in defense against intracellular bacteria
- PMID: 37429234
- PMCID: PMC10530505
- DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101805
Pyroptosis in defense against intracellular bacteria
Abstract
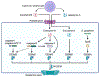
Pathogenic microbes invade the human body and trigger a host immune response to defend against the infection. In response, host-adapted pathogens employ numerous virulence strategies to overcome host defense mechanisms. As a result, the interaction between the host and pathogen is a dynamic process that shapes the evolution of the host's immune response. Among the immune responses against intracellular bacteria, pyroptosis, a lytic form of cell death, is a crucial mechanism that eliminates replicative niches for intracellular pathogens and modulates the immune system by releasing danger signals. This review focuses on the role of pyroptosis in combating intracellular bacterial infection. We examine the cell type specific roles of pyroptosis in neutrophils and intestinal epithelial cells. We discuss the regulatory mechanisms of pyroptosis, including its modulation by autophagy and interferon-inducible GTPases. Furthermore, we highlight that while host-adapted pathogens can often subvert pyroptosis, environmental microbes are effectively eliminated by pyroptosis.
Keywords: Autophagy; Environmental pathogen; Guanylate-binding protein; Host-adapted pathogen; Intracellular bacteria; Pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Girardin SE, Sansonetti PJ & Philpott DJ Intracellular vs extracellular recognition of pathogens – common concepts in mammals and flies. Trends Microbiol 10, 193–199 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Petit TJP & Lebreton A Adaptations of intracellular bacteria to vacuolar or cytosolic niches. Trends Microbiol 30, 736–748 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Gutierrez MG & Enninga J Intracellular niche switching as host subversion strategy of bacterial pathogens. Curr Opin Cell Biol 76, 102081 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

