Genome-wide association analysis and Mendelian randomization proteomics identify drug targets for heart failure
- PMID: 37429843
- PMCID: PMC10333277
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-39253-3
Genome-wide association analysis and Mendelian randomization proteomics identify drug targets for heart failure
Abstract
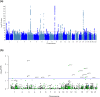
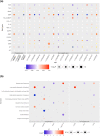
We conduct a large-scale meta-analysis of heart failure genome-wide association studies (GWAS) consisting of over 90,000 heart failure cases and more than 1 million control individuals of European ancestry to uncover novel genetic determinants for heart failure. Using the GWAS results and blood protein quantitative loci, we perform Mendelian randomization and colocalization analyses on human proteins to provide putative causal evidence for the role of druggable proteins in the genesis of heart failure. We identify 39 genome-wide significant heart failure risk variants, of which 18 are previously unreported. Using a combination of Mendelian randomization proteomics and genetic cis-only colocalization analyses, we identify 10 additional putatively causal genes for heart failure. Findings from GWAS and Mendelian randomization-proteomics identify seven (CAMK2D, PRKD1, PRKD3, MAPK3, TNFSF12, APOC3 and NAE1) proteins as potential targets for interventions to be used in primary prevention of heart failure.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Pharmacological blood pressure lowering for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease across different levels of blood pressure: an individual participant-level data meta-analysis. Lancet. 2021;397:1625–1636. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00590-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- I01 BX004821/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- MC_UU_00002/18/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- T32 HG002295/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_13046/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DK127083/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX001737/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U18 DP006711/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- I01 BX005831/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- MC_UU_12015/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R21 AI156161/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NIHR203330/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- I01 CX001025/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- U18DP006711/ACL/ACL HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

