Heart failure-induced cognitive dysfunction is mediated by intracellular Ca2+ leak through ryanodine receptor type 2
- PMID: 37429912
- PMCID: PMC10400432
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01377-6
Heart failure-induced cognitive dysfunction is mediated by intracellular Ca2+ leak through ryanodine receptor type 2
Abstract
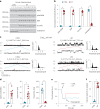
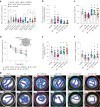
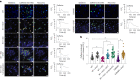
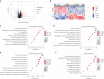
Cognitive dysfunction (CD) in heart failure (HF) adversely affects treatment compliance and quality of life. Although ryanodine receptor type 2 (RyR2) has been linked to cardiac muscle dysfunction, its role in CD in HF remains unclear. Here, we show in hippocampal neurons from individuals and mice with HF that the RyR2/intracellular Ca2+ release channels were subjected to post-translational modification (PTM) and were leaky. RyR2 PTM included protein kinase A phosphorylation, oxidation, nitrosylation and depletion of the stabilizing subunit calstabin2. RyR2 PTM was caused by hyper-adrenergic signaling and activation of the transforming growth factor-beta pathway. HF mice treated with a RyR2 stabilizer drug (S107), beta blocker (propranolol) or transforming growth factor-beta inhibitor (SD-208), or genetically engineered mice resistant to RyR2 Ca2+ leak (RyR2-p.Ser2808Ala), were protected against HF-induced CD. Taken together, we propose that HF is a systemic illness driven by intracellular Ca2+ leak that includes cardiogenic dementia.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Columbia University and A.R.M. own stock in ARMGO, a company developing compounds targeting RyR and have patents on Rycals. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


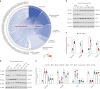
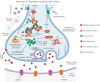
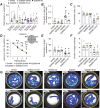
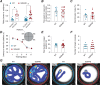


References
-
- Ambrosy AP, et al. The global health and economic burden of hospitalizations for heart failure: lessons learned from hospitalized heart failure registries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014;63:1123–1133. - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P, et al. Heart failure: preventing disease and death worldwide. ESC Heart Fail. 2014;1:4–25. - PubMed
-
- McParland C, Krishnan B, Wang Y, Gallagher CG. Inspiratory muscle weakness and dyspnea in chronic heart failure. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1992;146:467–472. - PubMed
-
- Huynh K. Heart failure: HF-induced diaphragmatic atrophy and weakness. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017;14:384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

