Global, regional, and national burden of heart failure associated with atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 37430216
- PMCID: PMC10334524
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-023-03375-9
Global, regional, and national burden of heart failure associated with atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Background: Heart failure is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide, and Atrial fibrillation (AF) is among many modifiable risk factors for heart failure. No estimates are available on the magnitude of the burden of heart failure associated with AF, and this study estimated the global, regional, and national burdens associated with AF.
Methods: We used the comparative risk assessment method to estimate the disease burden in terms of prevalence and years lived with disability (YLD). The population-attributable fraction for heart failure and AF was calculated from prevalence estimates of AF and the recalculated relative risks of heart failure associated with AF from a systematic review summarising the longitudinal association between AF and outcomes. The burden of heart failure was retrieved from the Global Burden of Disease database.
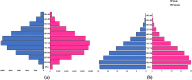
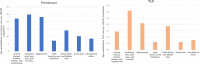
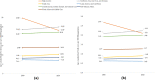
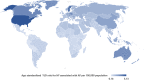
Results: Globally, 2.6% (95% uncertainty interval 1.3 to 4.7%) of the burden of heart failure is associated with AF. This was 1.5 (95% UI 0.6 to 3.2) million people in 2019, a 49.8% increase from 1990. The highest prevalence was from South-East Asia, East Asia and Oceania. The highest YLD was estimated for Central Europe, Eastern Europe and Central Asia. High-income countries showed a sharp decline in the age standardised prevalence and YLD rates from 1990 to 2019.
Conclusion: The burden of heart failure associated with AF has increased substantially over the past two decades despite the advances in AF management. However, falling prevalence and YLD rates of heart failure associated with AF in high-income countries over time indicate that reducing this burden is possible.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Global burden; Heart failure; National burden; Population attributable fraction; Regional burden.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atrial fibrillation and flutter as global drivers of heart failure: Burden and longitudinal trends over three decades.ESC Heart Fail. 2025 Jun 13. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.15344. Online ahead of print. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 40511537
-
Global and regional burden of ischemic stroke associated with atrial fibrillation, 2009-2019.Prev Med. 2023 Aug;173:107584. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2023.107584. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Prev Med. 2023. PMID: 37348767
-
Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study.Circulation. 2014 Feb 25;129(8):837-47. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005119. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Circulation. 2014. PMID: 24345399 Free PMC article.
-
Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014 Nov;11(11):639-54. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2014.118. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25113750 Review.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.Lancet Psychiatry. 2022 Feb;9(2):137-150. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00395-3. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35026139 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Traditional Chinese medicine challenging conventional Western medicine in cardiovascular diseases?Intern Emerg Med. 2025 Mar;20(2):345-348. doi: 10.1007/s11739-025-03892-9. Epub 2025 Feb 16. Intern Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 39956848 No abstract available.
-
The Atrial FibriLlatiOn Registry (FLOW-AF): Patient Characteristics, Treatment Patterns, and Outcomes in Egypt.Cardiol Ther. 2025 Jun;14(2):161-182. doi: 10.1007/s40119-025-00400-0. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Cardiol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40117063 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden of atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter and its attributable risk factors in adolescents and young adults, 1990-2021: insights from the global burden of disease study.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2543524. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2543524. Epub 2025 Aug 5. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40761146 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence and atrial fibrillation: A bibliometric analysis from 2013 to 2023.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 23;10(15):e35067. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35067. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Left Atrial Appendage Closure With Catheter Ablation vs. Ablation Alone on Outcomes of Atrial Fibrillation in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Nov 27;16(11):e74577. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74577. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39735150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, Gardner RS, Baumbach A, Böhm M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: developed by the task force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(36):3599–3726. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Institute for Health Matrix Evaluation (IHME). GBD Results Seatle, WA; 2020. Available from: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

