Effect of chemical disinfection on the dimensional stability of polyvinyl ether siloxane impression material: a systemic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37430254
- PMCID: PMC10331969
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-023-03168-8
Effect of chemical disinfection on the dimensional stability of polyvinyl ether siloxane impression material: a systemic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Polyvinyl ether siloxane (PVES) possesses ideal characteristics for making precise and accurate dental impressions. PVES dimensional stability owes to its better polymeric properties derived from its parent materials poly ethers and polyvinyl siloxanes. As recommended use of chemical disinfecting agents is getting more popular, there is a growing concern associated with the effect of disinfectants on PVES dimensional stability. This study was aimed to understand the PVES behavior when subjected to chemical disinfectants.
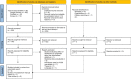
Materials and methodology: The data was collected from research studies retrieved from Google Scholar, Scopus, and PubMed using MeSH terms of keywords "vinyl polyether siloxane AND Disinfection" or (Vinyl polyether siloxane OR polyvinyl siloxane ether OR PVES) AND (disinfectant OR disinfection)" without any restriction to publication date. The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis) directions were observed during the data collection, screening of studies, and meta-analysis. The primary data were retrieved, and batch exported from databases using Harzing's Publish or Perish software; primary analysis was performed in Microsoft Excel, while statistical analysis for effect size, two-tailed p-values, and heterogeneity among studies was performed using Meta Essentials. The effect size was calculated using Hedge's g values at the 95% confidence level using the random-effects model. Heterogeneity among studies was measured using the Cochrane Q and I2.
Results and conclusion: Dental impressions made from the PVES elastomeric impression materials showed no significant changes in dimensional stability. Immersion in the chemical disinfectant for 10 min was associated with clinically irrelevant changes in the dimensions of the PVES impressions. Disinfection with sodium hypochlorite was associated with clinically significant changes in dimensions, with a two-tailed p-value of 0.049. Disinfection with 2-2.5% glutaraldehyde solution was not associated with any significant dimensional variability.
Keywords: Chemical disinfection; Glutaraldehyde; Hybrid elastomeric impression material; PVES; Sodium hypochlorite; Vinyl polyether siloxane.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Properties of a novel composite elastomeric polymer vinyl polyether siloxane in comparison to its parent materials: a systemic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Jan 9;24(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03830-1. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38195442 Free PMC article.
-
Effects chemical disinfectants on surface roughness of conventional impression materials used for dental prosthetic procedures.Niger J Clin Pract. 2022 Sep;25(9):1484-1489. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_1920_21. Niger J Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 36149208
-
Comparative Evaluation of the Effect of Chemical Disinfectants and Ultraviolet Disinfection on Dimensional Stability of the Polyvinyl Siloxane Impressions.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2019 Mar-Apr;9(2):152-158. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_406_18. Epub 2019 Apr 12. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2019. PMID: 31058065 Free PMC article.
-
3D evaluation of the effect of disinfectants on dimensional accuracy and stability of two elastomeric impression materials.Dent Mater J. 2018 Jul 29;37(4):675-684. doi: 10.4012/dmj.2017-097. Epub 2018 May 31. Dent Mater J. 2018. PMID: 29848853
-
Disinfection Procedures and Their Effect on the Microorganism Colonization of Dental Impression Materials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of In Vitro Studies.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Mar 16;9(3):123. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9030123. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35324812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of dimensional stability of novel VPES impression material at different time intervals with standard disinfectants.BMC Oral Health. 2024 May 18;24(1):579. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04323-5. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38762747 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional Dental Impressions vs. Impressions Reinforced with Rigid Mouthguards.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Apr 4;16(7):994. doi: 10.3390/polym16070994. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611252 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of Tear Strength Across Different Types of Maxillofacial Silicone Materials: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Jun;49(12):3372-3385. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-04832-w. Epub 2025 Apr 3. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40180644
-
How could mouthwashes affect the color stability and translucency of various types of monolithic zirconia? An in-vitro study.PLoS One. 2023 Dec 1;18(12):e0295420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295420. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 38039318 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing the influence of scanning speeds and distances on digital intraoral scans: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Evid Based Dent. 2025 Apr 10. doi: 10.1038/s41432-025-01135-6. Online ahead of print. Evid Based Dent. 2025. PMID: 40211050
References
-
- Varvara G, Sinjari B, Bernardi S, Turkyilmaz I, Malvezzi V, Piattelli M, Caputi S. Comparative surface detail reproduction for elastomeric impression materials: Study on reproducibility performance. Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents. 2021 Jan 1;35(1):161-9. - PubMed
-
- Mohammed DH, Fatalla AA, Jani GH. Comparison of Some Mechanical and Physical Properties of three Types of Impression Materials with Different Dental Implant Angulations. Biomedical and Pharmacology Journal. 2018 Sep 21;11(3):1359-68.
-
- Chauhan D, Singh D, Jadhav D, Swarup S, Ahuja S, Soni S. Assessment of accuracy of different materials used in impressions for fixed partial dentures. Eur J Molecular & Clin Med. 2021 Feb;4(09):3072–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

