Youth engagement in research: exploring training needs of youth with neurodevelopmental disabilities
- PMID: 37430378
- PMCID: PMC10332095
- DOI: 10.1186/s40900-023-00452-3
Youth engagement in research: exploring training needs of youth with neurodevelopmental disabilities
Abstract
Background: Authentic researcher-youth partnerships in patient-oriented research (POR) where the research responds to the needs expressed by youth themselves are essential to make research meaningful. While patient-oriented research (POR) is increasingly practiced, few training programs exist in Canada and none, to our knowledge, are tailored for youth with neurodevelopmental disabilities (NDD). Our primary objective was to explore the training needs of youth (ages 18-25) with NDD to enhance their knowledge, confidence, and skills as research partners. Our secondary objective was to identify the benefits and challenges of engaging youth with NDD in a POR approach.
Methods: Our team of four youth and one parent with lived experience [Youth Engagement in Research (YER) partners] and six researchers engaged in POR to investigate the primary objective via two phases: (1) individual interviews with youth living with NDD and (2) a two-day virtual symposium with focus groups with youth and researchers. Collaborative qualitative content analysis was employed to synthesize the data. Our secondary objective was assessed by asking our YER partners to complete the Public and Patient Engagement Evaluation Tool (PPEET) survey and participate in reflective discussions.
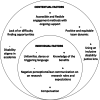
Results: Phase 1 participants (n = 7) identified various barriers and facilitators to their engagement in research and offered suggestions to meet their needs through minimizing barriers and integrating facilitators, which would subsequently enhance their knowledge, confidence, and skills as research partners. Informed by phase 1, phase 2 participants (n = 17) prioritized the following POR training needs: researcher-youth communication, research roles and responsibilities, and finding partnership opportunities. For delivery methods, participants stated the importance of youth representation, using Universal Design for Learning, and co-learning between youth and researchers. Based on the PPEET data and subsequent discussions, YER partners agreed that they were able to express views freely, feel that their views were heard, and that their participation made a meaningful difference. Challenges included scheduling difficulties, ensuring multiple methods for engagement, and working under short timelines.
Conclusion: This study identified important training needs for youth with NDD and for researchers to engage in meaningful POR, which can subsequently inform the co-production of accessible training opportunities with and for youth.
Keywords: Disability; Engagement; Inclusion; Patient-oriented research; Training; Youth.
Plain language summary
Partnerships between researchers and youth, known as patient-oriented research (POR), are needed to make sure research is meaningful to youth. Our main goal was to explore the training needs of youth (ages 18-25) with neurodevelopmental disabilities (NDD) to enhance their knowledge, confidence, and skills as research partners. To find out, our team of four youth and one parent with lived experience (YER partners) and six researchers completed this project in two parts: 1) interviews with youth and 2) a two-day virtual workshop with youth and researchers. Data from the two parts were reviewed to answer our question. We learned from Part 1 that the needs of participants can be met by providing support and reducing barriers in POR. From Part 2, the top three important topics in partnerships were: researcher-youth communication, research roles and responsibilities, and finding partnership opportunities. Participants in the workshop emphasized having different youth represented, using a framework that allows learning for everyone, and co-learning between youth and researchers in the creation of learning materials. Our second goal was to understand the benefits and challenges of our partnership. To assess, YER partners completed a survey and reflected about their experiences. YER partners agreed on being able to express views, feel that their views were heard, and that their participation made a meaningful difference. Challenges included scheduling difficulties, providing multiple ways to partner, and working under short timelines. Overall, the study described important POR needs for youth and researchers, which can inform future training opportunities.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Benefits, barriers and recommendations for youth engagement in health research: combining evidence-based and youth perspectives.Res Involv Engagem. 2024 Sep 2;10(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s40900-024-00607-w. Res Involv Engagem. 2024. PMID: 39223602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Working together in health research: a mixed-methods patient engagement evaluation.Res Involv Engagem. 2023 Aug 1;9(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s40900-023-00475-w. Res Involv Engagem. 2023. PMID: 37528438 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery and evaluation of simulations to promote authentic and meaningful engagement in childhood disability research.Res Involv Engagem. 2023 Jul 18;9(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s40900-023-00468-9. Res Involv Engagem. 2023. PMID: 37464394 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons learned in measuring patient engagement in a Canada-wide childhood disability network.Res Involv Engagem. 2024 Feb 7;10(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s40900-024-00551-9. Res Involv Engagem. 2024. PMID: 38326926 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid realist review of patient engagement in patient-oriented research and health care system impacts: part one.Res Involv Engagem. 2021 Oct 10;7(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s40900-021-00299-6. Res Involv Engagem. 2021. PMID: 34629118 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An umbrella review of reviews on challenges to meaningful adolescent involvement in health research.Health Expect. 2024 Feb;27(1):e13980. doi: 10.1111/hex.13980. Health Expect. 2024. PMID: 39102665 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a patient and public involvement and engagement group to support clinical trials in Pakistan: Initial lessons learned.Res Involv Engagem. 2024 Sep 27;10(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s40900-024-00635-6. Res Involv Engagem. 2024. PMID: 39334505 Free PMC article.
-
Benefits, barriers and recommendations for youth engagement in health research: combining evidence-based and youth perspectives.Res Involv Engagem. 2024 Sep 2;10(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s40900-024-00607-w. Res Involv Engagem. 2024. PMID: 39223602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development, implementation, and scalability of the Family Engagement in Research Course: a novel online course for family partners and researchers in neurodevelopmental disability and child health.Res Involv Engagem. 2024 Aug 5;10(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s40900-024-00615-w. Res Involv Engagem. 2024. PMID: 39103968 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing patient-oriented research training: participant perceptions of an online course.Res Involv Engagem. 2024 Sep 6;10(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s40900-024-00629-4. Res Involv Engagem. 2024. PMID: 39242586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research: Strategy for Patient-Oriented Research Patient Engagement Framework [Internet]. Canadian Institutes of Health Research. 2019. Available from: https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/48413.html
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous