Role of linked color imaging for upper gastrointestinal disease: present and future
- PMID: 37430400
- PMCID: PMC10565447
- DOI: 10.5946/ce.2023.015
Role of linked color imaging for upper gastrointestinal disease: present and future
Abstract
Techniques for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy are advancing to facilitate lesion detection and improve prognosis. However, most early tumors in the upper gastrointestinal tract exhibit subtle color changes or morphological features that are difficult to detect using white light imaging. Linked color imaging (LCI) has been developed to overcome these shortcomings; it expands or reduces color information to clarify color differences, thereby facilitating the detection and observation of lesions. This article summarizes the characteristics of LCI and advances in LCI-related research in the upper gastrointestinal tract field.
Keywords: Barrett esophagus; Image enhancement; Linked color imaging; Neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

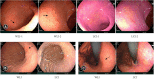
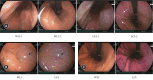
Similar articles
-
A prospective randomized tandem gastroscopy pilot study of linked color imaging versus white light imaging for detection of upper gastrointestinal lesions.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Sep;36(9):2562-2567. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15515. Epub 2021 Apr 12. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33811385 Clinical Trial.
-
Application of linked color imaging in the diagnosis of early gastrointestinal neoplasms and precancerous lesions: a review.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021 Jul 6;14:17562848211025925. doi: 10.1177/17562848211025925. eCollection 2021. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34285717 Free PMC article.
-
Linked Color Imaging Focused on Neoplasm Detection in the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract : A Randomized Trial.Ann Intern Med. 2021 Jan;174(1):18-24. doi: 10.7326/M19-2561. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Ann Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33076693 Clinical Trial.
-
Linked color imaging for the detection of early gastrointestinal neoplasms.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2019 Nov 1;12:1756284819885246. doi: 10.1177/1756284819885246. eCollection 2019. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31700545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Confocal laser endomicroscopy and molecular imaging in barrett esophagus and stomach.Clin Endosc. 2014 Jan;47(1):23-30. doi: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.1.23. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Clin Endosc. 2014. PMID: 24570880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: It is time to consider the quality of its outcomes.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Nov 21;29(43):5800-5803. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i43.5800. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 38074917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaise M, Kato M, Urashima M, et al. Magnifying endoscopy combined with narrow-band imaging for differential diagnosis of superficial depressed gastric lesions. Endoscopy. 2009;41:310–315. - PubMed
-
- Nakayoshi T, Tajiri H, Matsuda K, et al. Magnifying endoscopy combined with narrow band imaging system for early gastric cancer: correlation of vascular pattern with histopathology (including video) Endoscopy. 2004;36:1080–1084. - PubMed
-
- Yao K, Oishi T, Matsui T, et al. Novel magnified endoscopic findings of microvascular architecture in intramucosal gastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:279–284. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

