Real-Time Hybrid Test Control Research Based on Improved Electro-Hydraulic Servo Displacement Algorithm
- PMID: 37430679
- PMCID: PMC10224155
- DOI: 10.3390/s23104765
Real-Time Hybrid Test Control Research Based on Improved Electro-Hydraulic Servo Displacement Algorithm
Abstract
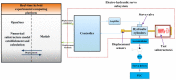
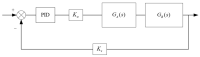
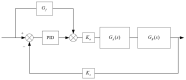
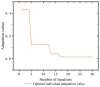
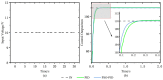
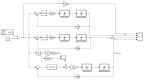
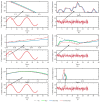
Real-time hybrid testing (RTH) is a test method for dynamic loading performance evaluation of structures, which is divided into digital simulation and physical testing, but the integration of the two may lead to problems such as time lag, large errors, and slow response time. The electro-hydraulic servo displacement system, as the transmission system of the physical test structure, directly affects the operational performance of RTH. Improving the performance of the electro-hydraulic servo displacement control system has become the key to solving the problem of RTH. In this paper, the FF-PSO-PID algorithm is proposed to control the electro-hydraulic servo system in real-time hybrid testing (RTH), which uses the PSO algorithm to operate the optimized PID parameters and the feed-forward compensation algorithm to compensate the displacement. First, the mathematical model of the electro-hydraulic displacement servo system in RTH is presented and the actual parameters are determined. Then, the objective evaluation function of the PSO algorithm is proposed to optimize the PID parameters in the context of RTH operation, and a displacement feed-forward compensation algorithm is added for theoretical study. To verify the effectiveness of the method, joint simulations were performed in Matlab/Simulink to compare and test FF-PSO-PID, PSO-PID, and conventional PID (PID) under different input signals. The results show that the proposed FF-PSO-PID algorithm effectively improves the accuracy and response speed of the electro-hydraulic servo displacement system and solves the problems of RTH time lag, large error, and slow response.
Keywords: FF-PSO-PID; PSO algorithm; composite control; electro-hydraulic servo; real-time hybrid test.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Shing P.B., Nakashima M., Bursi O.S. Application of Pseudodynamic Test Method to Structural Research. Earthq. Spectra. 1996;12:29–56. doi: 10.1193/1.1585867. - DOI
-
- Dermitzakis S.N., Mahin S.A. Development of Substructuring Techniques for On-Line Computer Controlled Seismic Performance Testing. University of California; Berkeley, CA, USA: 1985.
-
- Pan P., Nakashima M., Tomofuji H. Online Test Using Displacement–Force Mixed Control. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2005;34:869–888. doi: 10.1002/eqe.457. - DOI
-
- Bessa W.M., Dutra M.S., Kreuzer E. Sliding Mode Control with Adaptive Fuzzy Dead-Zone Compensation of an Electro-Hydraulic Servo-System. J. Intell. Robot Syst. 2010;58:3–16. doi: 10.1007/s10846-009-9342-x. - DOI
-
- Cerman O., Hušek P. Adaptive Fuzzy Sliding Mode Control for Electro-Hydraulic Servo Mechanism. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012;39:10269–10277. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2012.02.172. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

