Spurious Resonance of the QCM Sensor: Load Analysis Based on Impedance Spectroscopy
- PMID: 37430852
- PMCID: PMC10221602
- DOI: 10.3390/s23104939
Spurious Resonance of the QCM Sensor: Load Analysis Based on Impedance Spectroscopy
Abstract
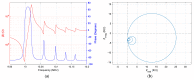
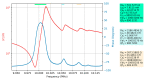
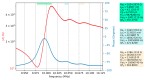
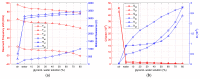
A research topic of equal importance to technological and application fields related to quartz crystal is the presence of unwanted responses known as spurious resonances. Spurious resonances are influenced by the surface finish of the quartz crystal, its diameter and thickness, and the mounting technique. In this paper, spurious resonances associated with fundamental resonance are studied by impedance spectroscopy to determine their evolution under load conditions. Investigation of the response of these spurious resonances provides new insights into the dissipation process at the QCM sensor surface. The significant increase of the motional resistance for spurious resonances at the transition from air to pure water is a specific situation revealed experimentally in this study. It has been shown experimentally that in the range between the air and water media, spurious resonances are much more attenuated than the fundamental resonance, thus providing support for investigating the dissipation process in detail. In this range, there are many applications in the field of chemical sensors or biosensors, such as VOC sensors, humidity sensors, or dew point sensors. The evolution of D factor with increasing medium viscosity is significantly different for spurious resonances compared to fundamental resonance, suggesting the usefulness of monitoring them in liquid media.
Keywords: AT-cut quartz crystal; QCM sensor; extended BVD electrical model; impedance spectroscopy; spurious resonances; virtual impedance analyzer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Advanced Impedance Spectroscopy for QCM Sensor in Liquid Medium.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Mar 17;22(6):2337. doi: 10.3390/s22062337. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336507 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Load on Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor Response Addressed Using Fractional Order Calculus.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;23(15):6768. doi: 10.3390/s23156768. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571551 Free PMC article.
-
Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Impedance Analysis Based on Virtual Instruments: Experimental Study.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Feb 15;22(4):1506. doi: 10.3390/s22041506. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214403 Free PMC article.
-
Quartz Crystal Microbalance With Dissipation Monitoring: A Powerful Method to Predict the in vivo Behavior of Bioengineered Surfaces.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018 Oct 30;6:158. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00158. eCollection 2018. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30425985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Imprinting Technology in Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) Sensors.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Feb 24;17(3):454. doi: 10.3390/s17030454. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28245588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bottom V.E. A History of the Quartz Crystal Industry in the USA; Proceedings of the 35th Annual Frequency Control Symposium; Abilene, TX, USA. 27–29 May 1981; [(accessed on 18 May 2023)]. pp. 3–12. Available online: https://ieee-uffc.org/about-us/history/uffc-s-history/a-history-of-the-q....
-
- Katzir S. Variations and Combinations: Invention and Development of Quartz Clock Technologies at AT&T. [(accessed on 18 May 2023)];Icon. 2016 22:78–114. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/44242742.
-
- Nacken R. Hydrothermal syntheses als grundlage für zuchtung von quartzkristallen. Chem. Ztg. 1950;74:745–749.
-
- Clairet A., Couteleau L., Laroche T., Boy J.-J. Experimental and theoretical results on SC-cut quartz resonators collectively realized on 4” wafers; Proceedings of the 2013 Joint European Frequency and Time Forum & International Frequency Control Symposium (EFTF/IFC); Prague, Czech Republic. 21–25 July 2013; pp. 662–665. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

