Prediction of the Physical Activity Level of Community-Dwelling Older Japanese Adults with a Triaxial Accelerometer Containing a Classification Algorithm for Ambulatory and Non-Ambulatory Activities
- PMID: 37430874
- PMCID: PMC10220935
- DOI: 10.3390/s23104960
Prediction of the Physical Activity Level of Community-Dwelling Older Japanese Adults with a Triaxial Accelerometer Containing a Classification Algorithm for Ambulatory and Non-Ambulatory Activities
Abstract
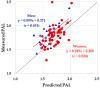
Accurate methods for the prediction of the total energy expenditure and physical activity level (PAL) in community-dwelling older adults have not been established. Therefore, we examined the validity of estimating the PAL using an activity monitor (Active style Pro HJA-350IT, [ASP]) and proposed correction formulae for such populations in Japan. Data for 69 Japanese community-dwelling adults aged 65 to 85 years were used. The total energy expenditure in free-living conditions was measured with the doubly labeled water method and the measured basal metabolic rate. The PAL was also estimated from metabolic equivalent (MET) values obtained with the activity monitor. Adjusted MET values were also calculated with the regression equation of Nagayoshi et al. (2019). The observed PAL was underestimated, but significantly correlated, with the PAL from the ASP. When adjusted using the Nagayoshi et al. regression equation, the PAL was overestimated. Therefore, we developed regression equations to estimate the actual PAL (Y) from the PAL obtained with the ASP for young adults (X) as follows: women: Y = 0.949 × X + 0.205, mean ± standard deviation of the prediction error = 0.00 ± 0.20; men: Y = 0.899 × X + 0.371, mean ± standard deviation of the prediction error = 0.00 ± 0.17.
Keywords: accelerometer; community-dwelling older adults; doubly labeled water; physical activity level; total energy expenditure.
Conflict of interest statement
Shigeho Tanaka received consigned research funds from Omron Healthcare Co., Ltd. The remaining authors do not have any relevant financial interests to disclose related to this research. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Validity of a triaxial accelerometer and simplified physical activity record in older adults aged 64-96 years: a doubly labeled water study.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018 Oct;118(10):2133-2146. doi: 10.1007/s00421-018-3944-6. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30019086
-
Validity of the Use of a Triaxial Accelerometer and a Physical Activity Questionnaire for Estimating Total Energy Expenditure and Physical Activity Level among Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: CLEVER-DM Study.Ann Nutr Metab. 2020;76(1):62-72. doi: 10.1159/000506223. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Ann Nutr Metab. 2020. PMID: 32172232
-
Predictors of Water Turnover in Older Adults: A Doubly Labeled Water- and Triaxial Accelerometer-Based Study.J Nutr. 2024 Jun;154(6):1750-1757. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2024.04.023. Epub 2024 Apr 20. J Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38649093
-
Impact of walking aids on estimating physical activity using a tri-axial accelerometer in frail older adults.BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2021 Jun 25;7(2):e001014. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2020-001014. eCollection 2021. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2021. PMID: 34249373 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise, energy expenditure and energy balance, as measured with doubly labelled water.Proc Nutr Soc. 2018 Feb;77(1):4-10. doi: 10.1017/S0029665117001148. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Proc Nutr Soc. 2018. PMID: 28724452 Review.
Cited by
-
A proof of concept for wear/non-wear classification using accelerometer data in daily activity recording: Synthetic algorithm leveraging probability and continuity of zero counts.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 22;19(10):e0309917. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309917. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39436886 Free PMC article.
-
Data Analytics in Physical Activity Studies With Accelerometers: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Sep 11;26:e59497. doi: 10.2196/59497. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39259962 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

