The effectiveness and safety of heat/cold therapy in adults with lymphoedema: systematic review
- PMID: 37431170
- PMCID: PMC11147455
- DOI: 10.1080/09638288.2023.2231842
The effectiveness and safety of heat/cold therapy in adults with lymphoedema: systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of this review is to assess the efficacy and safety of using heat and cold therapy for adults with lymphoedema.
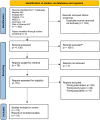
Methods: A multi-database search was undertaken. Only studies which included adults with lymphoedema who were treated with heat or cold therapy reporting any outcome were included. Screening, data extraction, and assessment of bias were undertaken by a single reviewer and verified by a second. Due to the substantial heterogeneity, a descriptive synthesis was undertaken.
Results: Eighteen studies were included. All nine studies which assessed the effects of heat-therapy on changes in limb circumference reported a point estimate indicating some reduction from baseline to end of study. Similarly, the five studies evaluating the use of heat-therapy on limb volume demonstrated a reduction in limb volume from baseline to end-of-study. Only four studies reported adverse events of which all were deemed to be minor. Only two studies explored the effects of cold therapy on lymphoedema.
Conclusions: Tentative evidence suggests heat-therapy may have some benefit in treating lymphoedema with minimal side effects. However, further high-quality randomised controlled trials are required, with a particular focus on moderating factors and assessment of adverse events.Implications for rehabilitationThis review highlights the potential benefit that heat therapy may have on reducing limb circumference and volume for adults with lymphoedema.There was no evidence that controlled localised heat therapy was unsafe.The current evidence-base is at a point where no specific clinical recommendations can be made.The use of heat therapy should only be applied as part of a methodologically robust study to treat lymphoedema.
Keywords: Lymphoedema; cold therapy; heat therapy; limb circumference; limb volume.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(26):1-149. doi: 10.3310/hta5260. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701099
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sleigh BC, Manna BL.. Lymphedema. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls; 2022.
-
- Rajan S, Venkatramani H.. Recent advances in management of lymphedema. J Skin Sex Transmit Dis. 2021;3:26–32. doi: 10.25259/JSSTD_15_2021. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical